Genome Instability & Disease Volume 2. Issue 3 & 4 简介
Volume 2 Issue 3
1. Role of NEDD8 and neddylation dynamics in DNA damage response | Yifan Luo, Yang Su & Feng Rao
Neddylation is a newly reported ubiquitin-like modification, but what is its function? Feng Rao and colleagues at the Southern University of Science and Technology, China, provide some answers for us, explaining how neddylation and de-neddylation serve to regulate the DNA damage response. They focus on the important role that NEDD8 plays in this regulatory mechanism, and speculate on areas for further research going forward.
DNA 损伤反应 (DDR)涉及到各种翻译后修饰,近年来,neddylation作为一种新的泛素样修饰引起广泛的关注。在这篇综述里,南方科技大学的饶枫课题组介绍了neddylation与去neddylation调控DDR的主要机制,尤其是NEDD8在调控中发挥重要作用,帮助我们更好的理解neddylation和DNA损伤反应的关系。

饶枫副教授:https://faculty.sustech.edu.cn/raof/
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00044-z
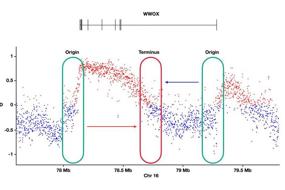
2. Somatic mosaicism in inherited bone marrow failure and chromosomal instability syndrome | Pronama Biswas & Rama Shankar Verma
Chromosomal instability syndrome (CIS) and hereditary bone marrow failure syndrome (IBMF) show great clinical heterogeneity and disease penetrance. These two types of diseases are often accompanied by somatic mosaicism, a key contributing factor in many monogenic disorders, and a predisposition to cancer. In this review, Pronama Biswas and Rama Shankar Verma summarize the latest research progress in understanding the underlying mechanisms of CIS and IBMF pathophysiology, which they hope will provide an important reference for early diagnosis and treatment.
染色体不稳定性综合征 (CIS)和 遗传性骨髓衰竭综合征(IBMF)在临床上表现出很大的异质性和疾病外显率,因此正确和准确的诊断是一个挑战。 在一些报道中这两类疾病往往伴随着体细胞嵌合现象,在这篇综述里,Pronama Biswas 和 Rama Shankar Verma概述了CIS和IBMF的研究进展,为这两类疾病以及癌症的早期检测筛查提供重要参考。

Rama Shankar Verma 教授:https://iitm.irins.org/profile/51101
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00041-2
3. BRCA1: a key player at multiple stages of homologous recombination in DNA double-strand break repair | Yidan Liu & Lin-Yu Lu
BRCA1 is an essential gene for maintaining genome stability and regulating various cell pathways. Here, Yida Liu and Lin-Yu Lu summarize the mechanism by which BRCA1 is recruited and participates in multiple stages in double strand break (DSB) repair. They also explain how homologous recombination defects caused by a deficiency in BRCA1 can be rescued by modulating DSB repair pathway choice. This review offers great insight into the function and mechanism of BRCA1 in the context of maintaining genome stability.
BRCA1 是维持基因组稳定性和调控癌症通路的重要基因,在这篇综述里,浙江大学的陆林宇团队总结了在DSB修复BRCA1被多阶段招募和参与调控的机制,以及如何通过调节DSB修复途径来挽救 BRCA1 缺陷引起的 HR 缺陷,帮助我们更好的了解BRCA1在维持基因组稳定性的功能与机制。

陆林宇教授:https://person.zju.edu.cn/lulinyu
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00042-1
4. Fanconi anemia pathway and its relationship with cancer | Chenchen Dan, Hongjing Pei, Buzhe Zhang, Xuan Zheng, Dongmei Ran & Changzheng Du
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare, inherited blood disease caused by mutations in genes that help repair DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICL). The FA regulatory pathway relies upon various post-translational modifications that maintain genome stability. Now, Changzheng Du and colleagues at the Southern University of Science and Technology, China, highlight the latest findings from recent FA gene discovery efforts. They outline the role of the FA pathway in carcinogenesis and how this might be manipulated in the context of cancer treatment.
范可尼贫血 (FA) 是一种由参与 DNA 链间交联 (ICL) 修复的基因突变引起的罕见遗传性血液病,其调控机制与维持基因组稳定性的多种翻译后修饰密切相关,在这篇综述里,来自南方科技大学的杜长征团队总结了FA 基因的发现历史和最新进展,并进一步讨论了 FA 通路在致癌和癌症治疗中的作用,对我们了解该领域的最新进展提供参考。

杜长征副教授:http://www.sustech.edu.cn/zh/facultys/duchangzheng.html
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00043-0
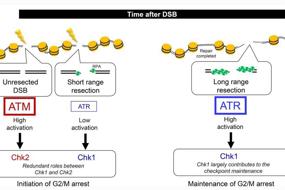
5. USP11 suppresses CHK1 activation by deubiquitinating CLASPIN | Hongchang Zhao, Zhifeng Wang, Min Zhu, Ji Liao & Xingzhi Xu
New data from Xingzhi Xu and colleagues show that when DNA replication is under stress, ubiquitin-specific protease 11 (USP11) is phosphorylated by ATR, allowing it to separate from CLASPIN and promote CLASPIN chromatin loading. The results from their intricate and comprehensive studies show that when CLASPIN binds chromatin, CHK1 activates and ultimately promotes genome stability. These exciting findings reveal an important and novel role for USP11 in negatively regulating CHK1 activation to maintain genome homeostasis.
CHK1是维持基因组稳定性关键的调控基因,深圳大学的许兴智团队发现在DNA复制面对压力时, 泛素特异性蛋白酶 11(USP11)被ATR磷酸化,与 CASPIN 分离,促进 CASPIN 染色质加载,使得CHK1 激活并最终促进基因组稳定性,揭示了USP11在维持基因组稳态过程中的重要作用与分子机制。

许兴智教授:https://med.szu.edu.cn/Item/2994.aspx
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00034-1
Volume 2 Issue 4
1. Structural insights into the role of DNA-PK as a master regulator in NHEJ | Siyu Chen, James P. Lees-Miller, Yuan He & Susan P. Lees-Miller
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is an important pathway to repair DNA double strand breaks. The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) is the main regulator of the NHEJ pathway. In this review, Susan P. Lees-Miller and colleagues from the University of Calgary, Canada, introduce the structure of NHEJ synaptic complexes — an evolutionarily conserved and functionally important YRPD motif. They focus on the work of Dr. Carl W. Anderson, who conducted early characterizations of DNA-PK, and then explain how the DNA-PKcs signaling cascade is necessary for specific and efficient assembly of the synaptic complex during NHEJ.
非同源末端连接 (NHEJ)是DNA双链断裂损伤修复的重要途径之一,而DNA-PKcs又是NHEJ通路的主要调节因子。在这篇综述里,来自加拿大卡尔加里大学的Susan P. Lees-Miller团队介绍了NHEJ 突触复合物的结构、进化上保守且功能重要的 YRPD 基序,以及 DNA-PKcs 的作用及其在 NHEJ 中的磷酸化作用,帮助我们更好的了解该领域的最新进展。

Susan P. Lees-Miller教授:https://cumming.ucalgary.ca/departments/bmb/profiles/dr-susan-p-lees-miller
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00047-w
2. The activation mechanisms of master kinases in the DNA damage response | Jianxiong Xiao, Qinhui Rao & Yanhui Xu
ATM, ATR and DNA-PK are considered the three most important kinases involved in the DNA damage response. Yanhui Xu and colleagues from Fudan University, China, now provide us with an update of the latest advances made in understanding the structures of these three kinases. They speculate on the role of the PIKK regulatory domain in their activation and discuss how recent advances, most of which have been made using cryo-electron microscopy, are informing us of their functions and regulatory mechanisms.
ATM、ATR 和 DNA-PK是DNA损伤反应(DDR)过程中最重要的三个激酶,在这篇综述里,来自复旦大学的徐彦晖团队向我们介绍了这三个激酶在结构方面的最新进展,帮助我们更好的了解这些结构的功能及其调控机制。

徐彦辉教授:https://xulab.fudan.edu.cn/index.htm
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00045-y
3. Microproteins: from behind the scenes to the spotlight | Meiqian Jiang, Huiqiang Lou & Wenya Hou
Microproteins containing fewer than 200 amino acids were once considered non-functional. However, in-depth research efforts making use of technological advances have concluded that numerous microproteins do indeed have biological functions. Dr. Wenya Hou and colleagues outline the latest advances in this emerging field of microproteins. In their review, they pay specific attention to the relevance of microproteins to diseases associated with genome stability.
少于 200 个氨基酸的微蛋白曾经被认为是无功能的,随着技术的发展和深入的研究,越来越多的微蛋白被鉴定和报道具有生物学功能。在这篇综述里,深圳大学的楼慧强教授、侯文雅博士团队介绍了微蛋白领域的最新进展,以及和基因组稳态相关疾病的相关性,帮助我们了解该领域的最新动态。


楼慧强教授 候文雅博士
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00040-3
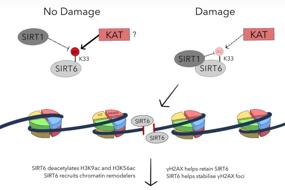
4. Regulation of Rothmund–Thomson syndrome protein RecQL4 functions in DNA replication by SIRT1-mediated deacetylation | Yuxia Yang, Wei Fan, Rong Wang, Rui Wang, Wei Gu & Jianyuan Luo
RecQL4 is a member of the RecQ DNA helicase family involved in DNA replication, recombination, and repair. New data from Jianyuan Luo and colleagues at Peking University, China, show that RecQL4 can be deacetylated by SIRT1, which in turn affects the initiation of DNA replication. These new findings provide great insight into how SIRT1 regulates both the cell cycle and DNA replication.
RecQL4是参与DNA复制、重组和修复的RecQ DNA解旋酶家族的成员,来自北京大学医学部的罗建沅团队发现RecQL4能被SIRT1去乙酰化,进而影响DNA的复制启动,该发现为SIRT1如何调控细胞周期、以及如何调节DNA复制提供了新的见解。

罗建沅教授:http://sbms.bjmu.edu.cn/jsdw/bssds/dsjs/132268.htm
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00048-9
5. SIRT7 is a deacetylase of N4-acetylcytidine on ribosomal RNA | Chenzhong Xu, Jin Zhang, Jie Zhang & Baohua Liu
SIRT7 is a NAD+-dependent protein deacetylase that has an important role in modulating genome stability, circadian rhythmicity, metabolism, and aging. New data produced by Baohua Liu and colleagues at Shenzhen University, China, support that SIRT7 can deacetylate ribosomal (r)RNA ac4C without relying on NAD+. Their exciting findings support SIRT7's importance in epigenetic transcriptional regulation, and in particular, the epitranscriptional regulation of aging.
SIRT7 已知是一类NAD+依赖的蛋白质去乙酰化酶,在基因组稳定性、昼夜节律、新陈代谢和衰老中发挥重要作用。深圳大学的刘宝华团队首次发现SIRT7能够去乙酰化核糖体(r)RNA ac4C,并且不依赖于NAD+,该发现为SIRT7的表观遗传转录调控做了重要补充,为研究SIRT7提供新的思路。

刘宝华教授:https://med.szu.edu.cn/Item/327.aspx
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00046-x

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册