Genome Instability & Disease Volume 3. Issue 5 简介
1. Accurate prediction of stomach adenocarcinomas of poorest and best prognosis with a combination of gene expression and clinical signatures | Lingyu Qiu, Huayu Kang, Jielin Yang, Yidong Zheng, Aiyue Chen, Chunlin Chen, Xinlong Wang, Qiongfang Fang, Wei-Guo Zhu, Ou Sha & Yejun Wang
Genetic heterogeneity hampers the identification of biomarkers for stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD). In this study, Professors Yejun Wang, Ou Sha and colleagues from Shenzhen University, China, developed a strategy that improves the likelihood of identifying prognostic gene signatures of STAD. In brief, their strategy was based on bi-end stratification combined with supervised comparison and LASSO regression. By this approach, they identified 12 genetic signatures associated with a good STAD prognosis, and 12 signatures associated with a poor prognosis. Subsequent modelling allowed the researchers to differentiate patients with STAD based on their predicted prognosis. Their resulting two, multi-gene models might serve to guide clinical treatment decisions.
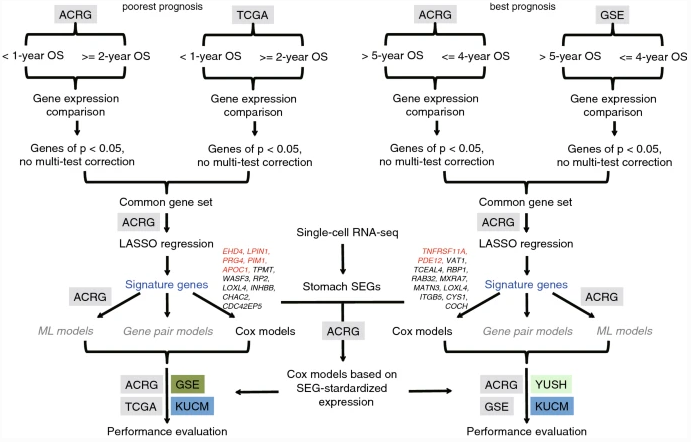
Fig. 1 Design of the research to identify and apply the STAD prognosis related gene expression signatures.
遗传异质性是影响判断胃腺癌(STAD)预后的重要原因。来自深圳大学的汪业军教授和沙鸥教授报道了一种结合监督比较和LASSO回归的双端分层策略,可以提高识别预后基因特征的统计能力,并开发了两个实用的多基因模型,有效地预测了预后最差和最好的STAD病例,为胃腺癌的临床治疗提供参考。

汪业军教授

沙鸥教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00077-y
2. FAM135B: a new player in DNA damage response| Chunyu Song & Lin Deng
The ATM-TIP60 complex allows cells to rapidly respond to double strand breaks (DSBs), but how it achieves this effect is not fully understood. Now, Lin Deng and colleagues from Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, China, have identified a new regulator of the ATM-TIP60 complex: FAM135B. Through their molecular analyses, the researchers show that FAM135B interacts with and maintains the TIP60-ATM reservoir under normal conditions. In response to DNA damage, FAM135B dissociates from the complex and degrades, thus releasing the complex to respond to the damage. These findings implicate FAM135B as a key regulator of DSB repair, and help clarify the kinetics of the ATM-TIP60 complex.
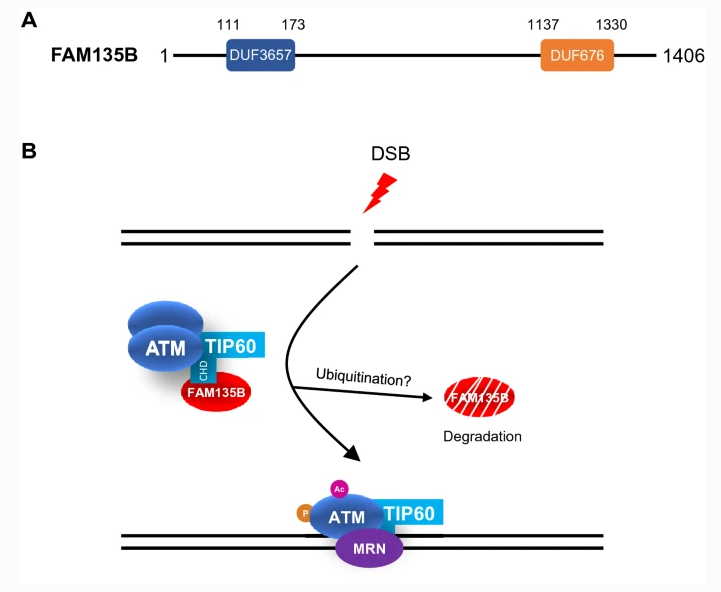
Fig. 2 Structure of FAM135B and its function in DNA damage response.
ATM-TIP60是细胞快速应对DSB的重要复合物。深圳湾实验室的邓麟和同事报道了FAM135B调节ATM-TIP60参与DSB修复过程的重要机制:正常情况下FAM135B与TIP60-ATM结合并维持静息状态,当细胞发生DNA双链断裂时,DAM135B从复合物脱落并被降解,被激活的ATM-TIP60与MRN形成新的复合物并附着在断裂处,执行修复功能。该发现揭示了FAM135B在DNA双链断裂损伤修复中的调控作用,对ATM-TIP60如何被募集到DSB做了新的诠释。

邓麟教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00079-w
3.G-quadruplex and 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine across the genome: methodologies and crosstalk| Jiao An, Mengdie Yin & Jinchuan Hu
G-quadruplex (G4) is a non-standard secondary DNA structure that is predominantly found at guanine (G)-rich, transcriptional regulatory regions in the genome. This secondary structure seems to have roles in genome integrity, by regulating transcription and other key cellular processes. Yet because G has the lowest redox potential among the four nucleobases, this region is also the most prone to oxidative damage. The result is the formation of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (OG) following G exposure to reactive oxygen species. In this review, Professor Jinchuan Hu and colleagues from Fudan University, China summarize how recent advances in genome-wide mapping of G4 and OG have allowed us to understand their potential crosstalk at the genomic level to regulate transcription.
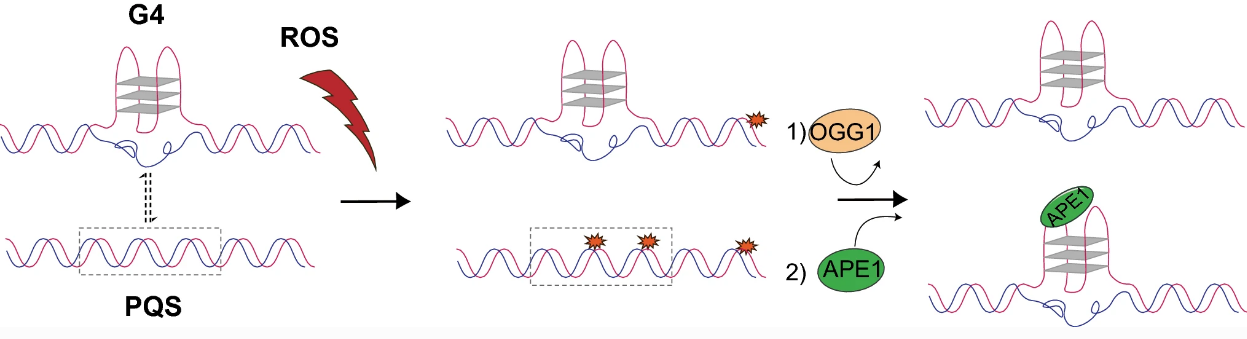
Fig. 3 A proposed model of the crosstalk between OG and G4.
DNA上富含G的区域容易出现G-四链体(G4,一种非规范的DNA二级结构,富含转录调控区和端粒), 同时,由于G在四个碱基中具有最低的氧化还原电位,该区域也最容易发生氧化损伤,其中最常见的氧化损伤是8-oxo-7,8-二氢鸟嘌呤(OG)。在这篇综述里,来自复旦大学的胡晋川教授和同事向我们介绍了G4和OG全基因组定位的最新进展,并讨论了它们在基因组水平上的相互串扰作用。

胡晋川教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00082-1
4. New insights into the mechanism of RPA in preserving genome stability| Simin Zhang, Xuejie Wang, Han Zhao, Jingyao Shi & Xuefeng Chen
Single stranded DNA (ssDNA) is produced during the process of transcription, DNA replication, repair, and recombination. Replication protein A (RPA) maintains ssDNA from enzymolysis and coordinates various DNA metabolic processes by dynamically binding to ssDNA or proteins. In this review, Professor Xuefeng Chen and colleagues from Wuhan University, China explain the roles of RPA in regulating replication, repair, nucleosome assembly, rDNA transcription, chromatin epigenetic landscape, and chromosome segregation. They also explain the mechanism of RPA turnover at replication forks or DNA lesions. This review serves as an excellent resource to better understand the functions and roles of RPA in protecting genome integrity.
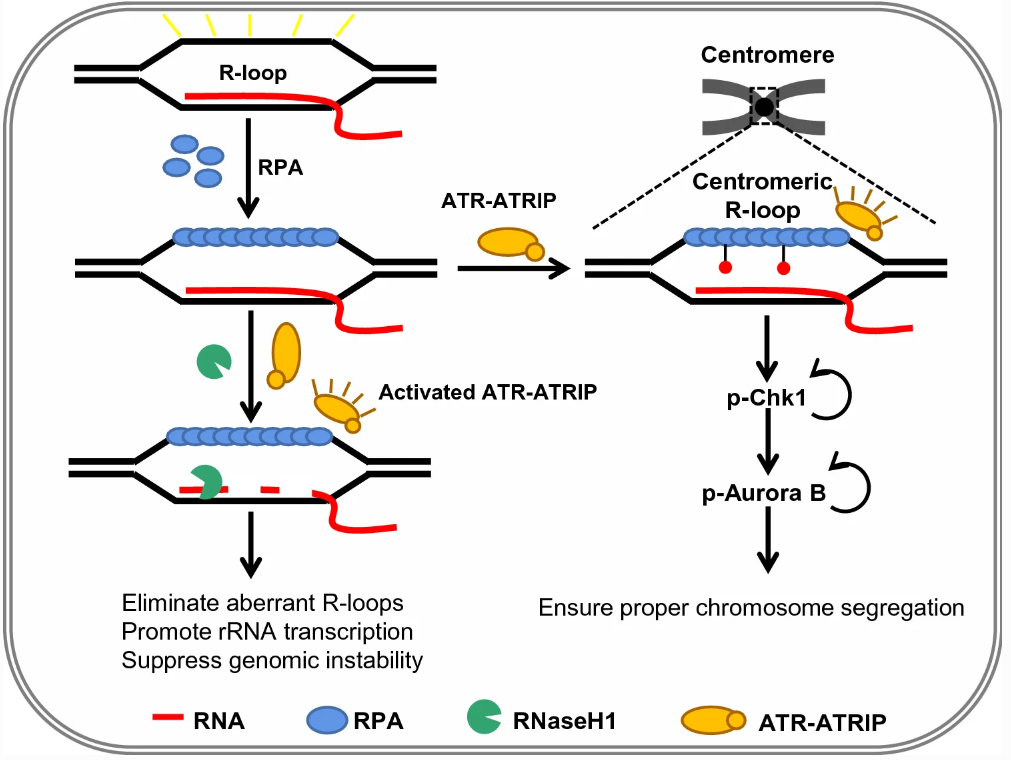
Fig. 4 The interaction of UfSP2 with the MRN complex is regulated by ATM-mediated phosphorylation
细胞在转录、DNA复制、修复和重组过程中会产生单链DNA(ssDNA),复制蛋白A(RPA)通过与ssDNA或蛋白质的动态结合,维持ssDNA免受酶解以及协调各种DNA代谢过程。在这篇综述里,武汉大学的陈学峰教授和同事向我们介绍了RPA在调节复制、修复、核小体组装、rDNA转录、染色质表观遗传和染色体分离方面的作用的最新进展,帮助我们更好地理解RPA在保护基因组完整性的功能和作用。

陈学峰教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00085-y
5. Defective replication stress response linked to microcephaly|SAjinkya S. Kawale & Lee Zou
Congenital microcephaly (MCPH) is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic disease. More than 40% of affected patients carry mutations in the ASPM gene. Recent work led by Professor Xingzhi Xu of Shenzhen University, China showed that under conditions of replication stress, the scaffold protein ASPM, promotes TopBP1 and RAD9 recruitment to replication forks, permitting ATR-CHK1 activation( Xingxuan Wu et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022 Oct 4;119(40):e2203783119.). They also found that ASPM can block replication forks, preventing DNA strand degradation by the nuclease MRE11, thus ensuring genome stability. In this commentary, Lee Zou and Ajinkya Kawale, from Harvard Medical School, USA, discuss the important role of ASPM in DNA replication. They emphasize that defective replication stress is a potential hallmark of MCPH pathogenesis, and thus might guide MCPH etiology and treatment.
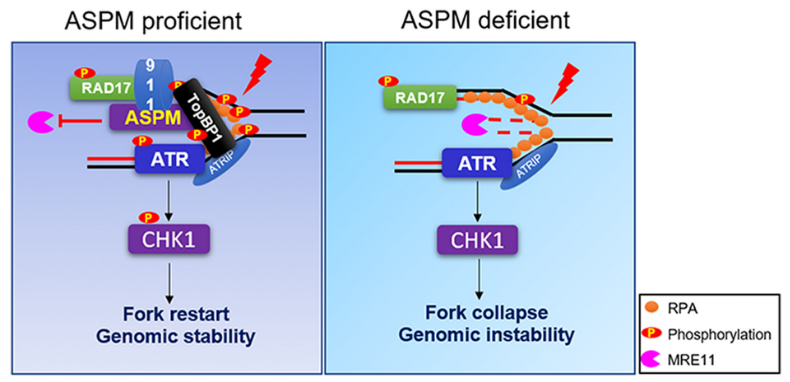
Fig. 5 Working model of ASPM on ATR-CHK1
先天性小头畸形 (Congenital Microcephaly,MCPH) 是一种罕见的常染色体隐形遗传病,研究发现,超过40%的MCPH患者异常纺锤状小头相关基因ASPM发生了突变。近期,深圳大学的许兴智教授和同事在PNAS上报道了ASPM作为支架蛋白促进TopBP1和RAD9在复制叉上的募集,进而促进复制胁迫下ATR-CHK1信号轴的活化,他们还发现ASPM可以被募集到阻滞的复制叉,避免新合成DNA链被核酸酶MRE11降解,维持复制叉的稳态,确保基因组的稳定以避免肿瘤等疾病的发生。对此,哈佛大学医学院DNA复制胁迫领域国际著名教授Lee Zou进行了点评,指出ASPM在DNA复制过程中的重要作用,强调了复制胁迫的缺陷与先天性小头畸形致病机制存在关联,为MCPH的病因和治疗提供参考。

Lee Zou教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00084-z

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册