Genome Instability & Disease Volume 4. Issue 1 简介
1. MutS and MutL sliding clamps in DNA mismatch repair | Xiao-Peng Han, Xiao-Wen Yang & Jiaquan Liu
Nucleotide mismatches arise during DNA replication and constitute a basic cause of DNA damage. Higher eukaryotes have evolved a highly sophisticated DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway, which triggers apoptosis in response to these mismatches to ensure genome stability. In this review, Professor Jiaquan Liu and colleagues from the Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China, summarize recent biophysical research on the MMR core components, MutS (MSH) and MutL (MLH/PMS), which sense DNA damage. They focus on how the unique conformations of these proteins effectively coordinate the MMR response.
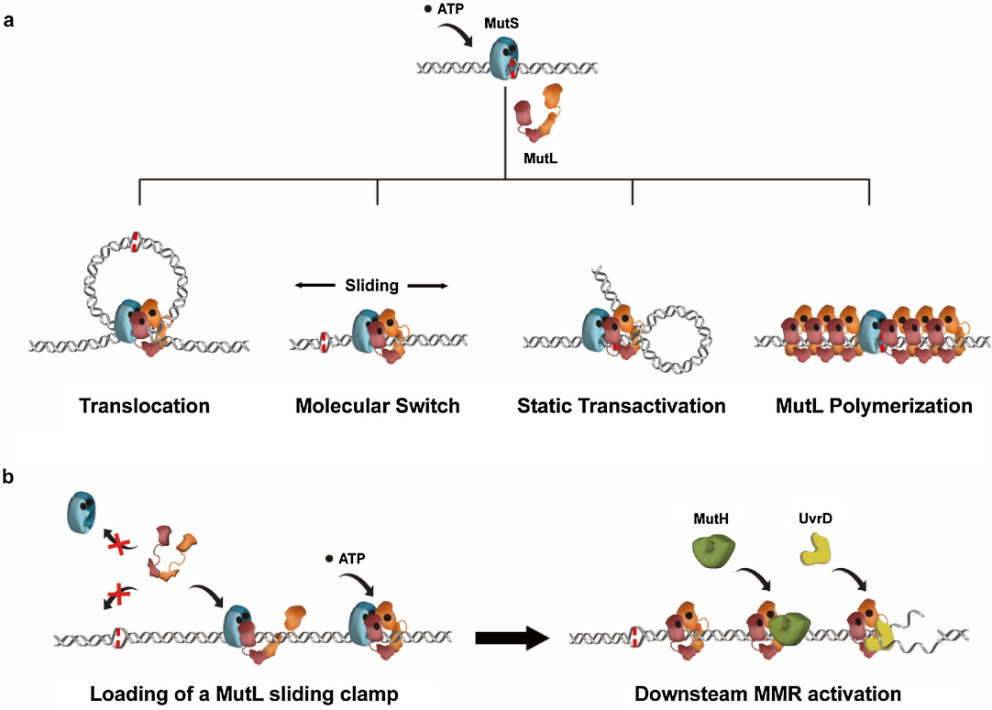
Fig.1 MMR models. a Historical models of MMR initiation. b A molecular switch model of the complete E. coli MMR.
DNA复制过程中出现的核苷酸错配,是导致基因突变的原因之一。在高等真核生物中,高度保守的MutS(MSH)和MutL(MLH/PMS)同源物启动了DNA错配修复(MMR),触发细胞凋亡以应对核苷酸错配造成的DNA损伤。在这篇综述里,来自中科院上海生物化学与细胞生物研究所的刘珈泉教授和同事总结了MMR核心成分的最新研究,重点从蛋白质构象来探讨MSH和MLH/PMS蛋白在MMR发挥作用的机制。

刘珈泉教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00094-x
2. Mitochondrial DNA mutation affects the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells with metabolism modulation| Juntao Qi, Qi Long, Yang Yuan, Yanshuang Zhou, Jian Zhang, Zifeng Ruan, Liang Yang, Yi Wu, Ge Xiang, Wei Li, Hao Wu, Shiwei Du & Xingguo Liu
In mammalian cells, mitochondria are the only organelle outside of the nucleus to contain DNA. Mutations to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can cause many serious diseases. Xingguo Liu and colleagues at the Guangzhou Institute of Biomedical and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, previously reported that mtDNA mutations aggravate the aging of the female reproductive system. Now, the researchers have studied the underlying mechanisms, using embryonic stem cells (ESCs) containing a large number of mtDNA (but not genomic DNA) mutations. By this approach, they aimed to learn more about how mtDNA mutations can affect stem cell pluripotency. Interestingly, they found that mtDNA mutations can lead to down-regulated oxidative phosphorylation, causing mitochondria to subsequently produce high levels of reactive oxygen species. The overall effect was an imbalance between pluripotency and totipotency of ESCs. These new data provide a new starting point to design interventions for mtDNA-mediated diseases.
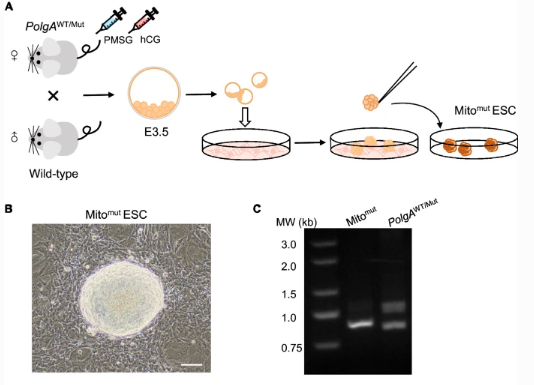
Fig. 2Generating ESCs carrying mtDNA mutations from Polg mutant mice.
在哺乳动物细胞中,线粒体是细胞核外唯一含有DNA的细胞器。线粒体DNA(mtDNA)突变会导致很多严重的疾病。中科院广州生物医药与健康研究院的刘兴国研究员课题组此前报道mtDNA突变加剧了女性生殖的衰老,为了进一步研究其内在机制,作者制备含有大量mtDNA突变而不影响基因组DNA的胚胎干细胞(ESC),发现mtDNA突变会导致能量代谢中氧化磷酸化的下调,引起线粒体产生高水平的ROS(氧化自由基),进而影响ESCs的多能性和全能性的平衡。该研究揭示了线粒体DNA(mtDNA)突变加剧了女性生殖衰老的原因,对相关疾病的治疗提供了参考。

刘兴国研究员
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00093-y
3. Histone methyltransferase GLP epigenetically activates GPCPD1 to sustain cancer cell metastasis and invasion | He Wen, Minghui Shu, Jia-Yi Chen, Xiaofan Li, Qian Zhu, Jun Zhang, Yuan Tian, Xiaopeng Lu & Wei-Guo Zhu
Aberrant choline metabolism has been associated with many diseases, including cancer. Glycerophosphate choline phosphodiesterase 1 (GPCPD1) is the key enzyme needed to cleave glycerophosphate choline (GPC) to produce choline. Whether and how GPCPD1 is epigenetically regulated is unclear. Here, Professor Wei-Guo Zhu and colleagues at Shenzhen University, China, provide new data showing that the histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) methyltransferase GLP permits the transcriptional activation of GPCPD1, together with the joint action of the transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5). Through a series of in vitro experiments, they saw that by this mechanism, GPCPD1 transcription raises choline levels, which in turn promotes tumor cell migration and invasion. These findings highlight the potential of targeting GLP and KLF5 in future cancer treatments.
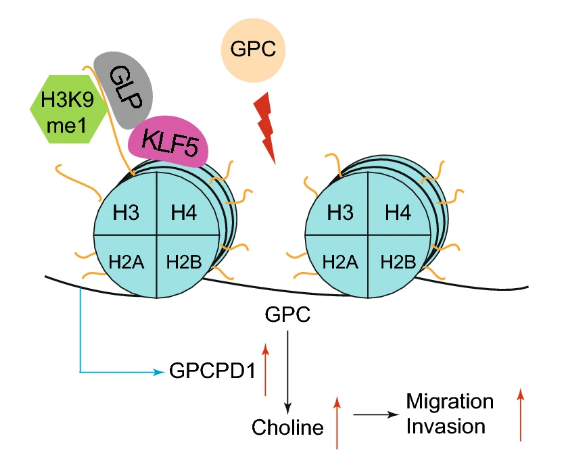
Fig. 3 After GPC treatment, GLP modifies H3K9 mono-methylation and recruits KLF5 to the GPCPD1 promoters to activate its transcription and permit choline biosynthesis, resulting in heightened migration and invasion capacity of cancer cells.
胆碱代谢与肿瘤在内的多种疾病密切相关。甘油磷酸胆碱磷酸二酯酶1(GPCPD1)是裂解甘油磷酸胆碱(GPC)产生胆碱关键的酶,GPCPD1是否以及如何受表观遗传调控仍在很大程度上未知。深圳大学的朱卫国教授团队报道了组蛋白H3赖氨酸9(H3K9)甲基转移酶GLP在转录因子Krüppel样因子5(KLF5)共同作用下,转录激活GPCPD1并促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭,提示GLP和KLF5可能是未来癌症治疗潜在的靶点。

朱卫国教授
全文链接: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00083-0
4. DYNLL1 transcript abundance decreases during oocyte and follicular growth and is associated with fertility in mice| Caglar Berkel & Ercan Cacan
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) are two repair pathways activated by cells following detection of a DNA double strand break (DSB). NHEJ can repair DSBs quickly but is prone to errors, while HR is slower but more accurate. In this paper, Professor Caglar Berkel and Professor Ercan Cacan from Tokat Gaziosmanpasa University, Turkey, show that the ovaries of highly fertile mice with increased ovulation express low Dynein light chain 1 (DYLL1) levels compared to wild-type control mice. They also show that the abundance of DYLL1 transcripts gradually decreases in these mice during oocyte and follicle growth. When the researchers induced ovulation with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) treatment, they saw a reduction in the level of DYLL1 mRNA transcription in the mouse cumulus-oocyte complex. They speculate, therefore, that DYLL1 might promote NHEJ and inhibit HR. If so, these findings reveal the important role of low levels of DYLL1 in maintaining the stability of mouse genome by ensuring oocyte quality and fertility.
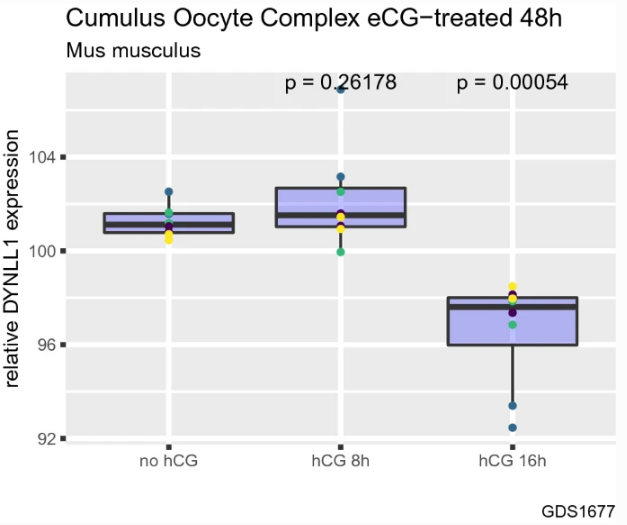
Fig. 4 Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) decreases DYNLL1 mRNA transcript levels in cumulus oocyte complexes in mice.
细胞面对DNA双链断裂(DSB)采用的两种主要修复途径分别为非同源末端连接(NHEJ)修复和同源重组(HR)修复,其中NHEJ能够快速修复但容易出错,HR则缓慢而准确。细胞采用何种修复方式应对DSB受到多种因素的调控,从而影响细胞的最终命运。来自土耳其Tokat Gaziosmanpasa大学的Caglar Berkel和Ercan Cacan教授发现DYLL1(Dynein轻链1)能够促进NHEJ和抑制HR,从而采用快速而易出错的修复方式。他们发现高生育力小鼠的卵巢具有较低的DYLL1,DYLL1转录物丰度在小鼠卵母细胞和卵泡生长期间逐渐降低,用人绒毛膜促性腺激素(hCG)诱导排卵会降低小鼠卵丘-卵母细胞复合体中DYLL1 mRNA转录水平,揭示了低水平的DYLL1对维持小鼠基因组稳定性,有助于更好的生育性能的重要作用。

Ercan Cacan教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00096-9

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册