Genome Instability & Disease Volume 4. Issue 3 简介
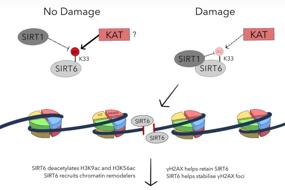
1. PARP molecular functions and applications of PARP inhibitors in cancer treatment | Yuhan Guo, Boyang Fan & Mo Li
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation (PARylation) is a post-translational modification that is catalyzed by poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). This modification is essential for many biological processes to proceed efficiently and effectively, including DNA damage repair, chromatin remodeling, programmed cell death, RNA regulation, and PAR-dependent ubiquitination. In this review, Professor Mo Li and colleagues from Peking University Third Hospital (China) focus on PARP1, first summarizing its important biological functions and then highlighting how PARP1 inhibitors can be applied to cancer treatment. They also discuss the ongoing issues regarding PARP1 inhibitor drug resistance.
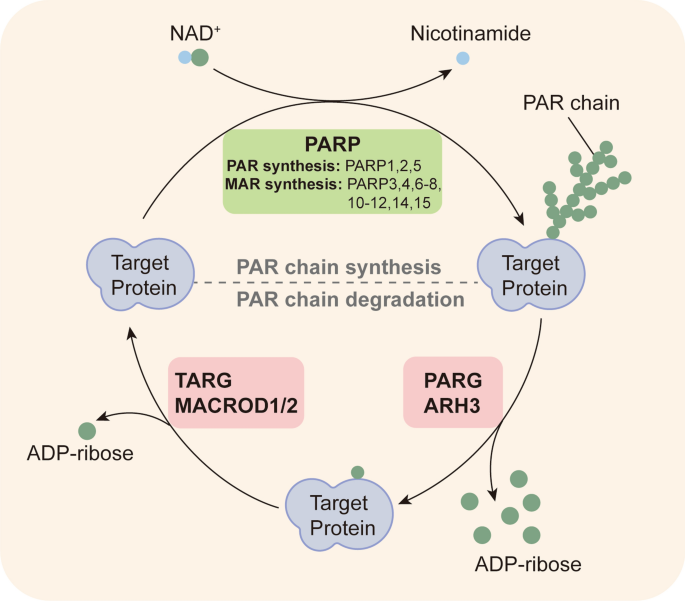
Fig.1 Dynamic synthesis and degradation of PAR chain.
聚腺苷二磷酸核糖基化(PARylation)是一种由聚腺苷三磷酸核糖聚合酶(PARP)催化的翻译后修饰,与许多生物过程有关,包括DNA修复、染色质重塑、程序性细胞死亡、RNA调节和PAR依赖的泛素化。在这篇综述里,来自北京大学第三医院李默教授,向我们总结了PARP1的重要功能,并重点介绍了PARP抑制剂在癌症治疗中的应用以及耐药问题,帮助我们了解该领域的最新进展。

李默教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00100-w
2. Identification of a novel inflammation-related gene signature for predicting inflammatory breast cancer survival| Weiyu Bai, Qinggang Hao, Zhimeng Zhang, Bingxing Han, Huilin Xiao, Dong Chang, Yun Zhu, Junling Shen & Jianwei Sun
Breast cancer is the most common cancer type and ranks second for cancer-related deaths in women. Now, Professor Jianwei Sun and colleagues from Yunnan University (China) have shown that it is possible to categorize patients with breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA) into high- and low-risk groups, depending on their level of inflammation. Specifically, they found that BRCA patients in the high-risk group have a high M2 macrophage abundance and tumor mutation burden (TMB). Moreover, signaling pathways related to inflammatory and immune responses were activated in these patients. Interestingly, they also found that PD.0332991 and ROSCOVITINE therapeutics were most effective in patients with low-risk inflammatory BRCA, while Bicalutamide and Imatinib were most effective in those with high-risk inflammatory BRCA. This categorization model thus seems to accurately predict the prognosis of BRCA subtypes, and might ultimately be used to help guide chemotherapeutic options for affected patients.
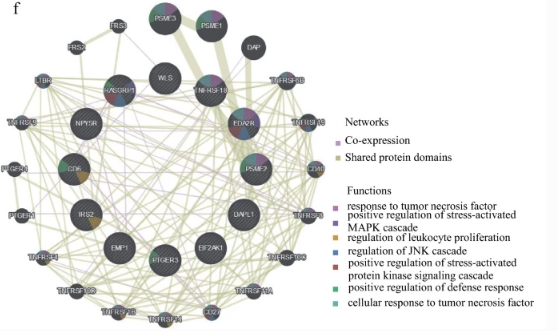
Fig.2 Protein–protein interactions of hub genes at the Gene MANIA.
乳腺癌是女性癌症相关死亡排名第二的常见癌症。来自云南大学的孙建伟教授团队通过数据库筛选分析,发现炎症水平高危人群中的乳腺癌症患者具有较高的巨噬细胞丰度和肿瘤突变负荷(TMB),炎症反应和免疫反应相关的信号通路被激活。团队构建的模型准确预测了乳腺癌症患者亚型的预后,为临床用药提供参考,帮助患者获得最佳的化疗方案。

孙建伟教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00102-8
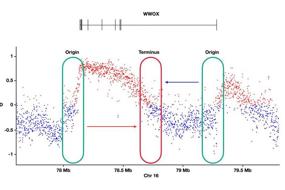
3. Proximity RNA labeling reveals functions of lncRNA in DNA damage response | Weili Li, Zhongxia Li, Zhiwen Deng, Jie Zhai, Shuzhen Han & Xiangyu Liu
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) participate in various physiological processes, including maintaining genomic stability. However, the underlying mechanisms determining how lncRNA's respond to DNA damage are unclear. In this study, Research Investigator Xiangyu Liu and colleagues from Shenzhen University (China), tested a method by which proximal lncRNAs of the DNA damage marker γH2AX are labelled by antibody-mediated protein a-ascorbic acid peroxidase 2 (APEX2). They found that several lncRNAs co-localized at DNA damage sites. These lncRNAs included BGL3 (that is known to bind BARD1) and SNHG12 (that is known to bind DNA-PK). Indeed, knockout of SNHG12 rendered HeLa and HCT116 cancer cells sensitive to irradiation. These findings thus provide a proof-of-principal that this method might be used to explore the roles of lncRNAs in the DNA damage response.
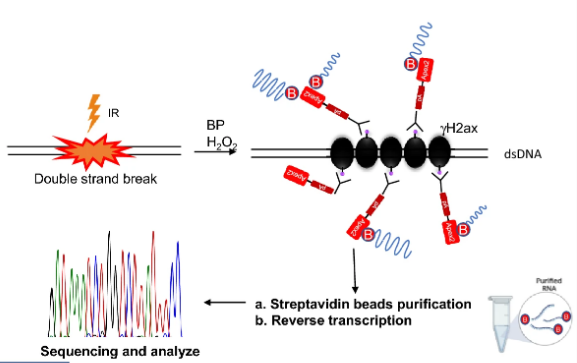
Fig. 3 Process of proximity RNA labeling around DNA damage sites.
长非编码RNA(lncRNA)参与各种生理过程,包括维持基因组稳定性。然而,决定lncRNA如何对DNA损伤做出反应的潜在机制尚不清楚。深圳大学的刘向宇研究员报道了一种新的方法,通过抗体介导的α-抗坏血酸过氧化物酶2(APEX2)标记DNA损伤标记物γH2AX的近端lncRNA。 他们发现几个lncRNA共同定位在DNA损伤位点。这些lncRNA包括BGL3(已知结合BARD1)和SNHG12(已知结合DNA-PK)。他们发现SNHG12基因敲除使HeLa和HCT116癌症细胞对辐射敏感。该方法可用于探索lncRNA在DNA损伤反应中的作用。

刘向宇研究员
全文链接: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00099-0
4. Common hotspots of cancer chemotherapy| Adekunle Fiyin Ademikanra, Olutayo Micheal Oyewole & Azeemat Olanrewaju Olayiwola
Huge advances have been made over the past decades in understanding the molecular, cellular and genetic drivers of cancer, yet cancer remains a major health burden worldwide. In this review, Dr. Adekunle Fiyin Ademikanra and colleagues from the Department of Biology at San Diego State University (USA) provide an overview of how cancers arise, explaining the main causes (cellular, genetic, and epigenetic alterations), classifications (carcinoma, sarcoma, lymphoma & leukaemia, blastoma, and germ cell tumours), clinical manifestations, and treatment methods. The authors then focus on the functions of the most commonly used chemotherapy regimens and other treatment options. Finally, they discuss the nature of cancer hotspots - areas of tumor DNA that are he most susceptible to genetic alteration.
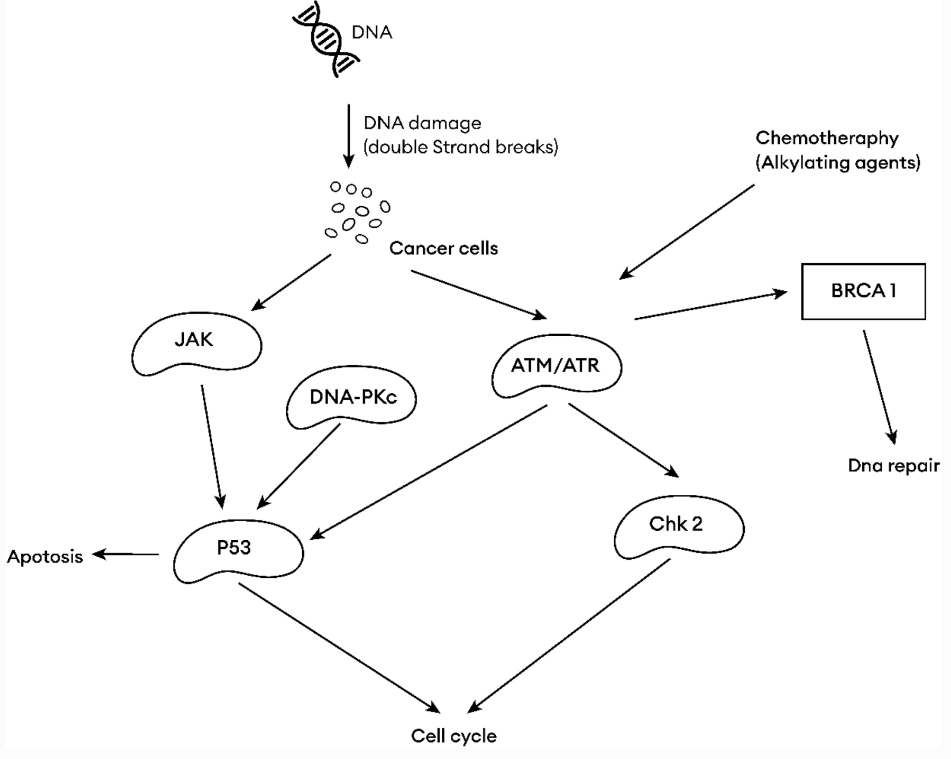
Fig. 4 Common hotspots targeted by cancer chemotherapies.
过去几十年,我们在了解癌症的分子、细胞和基因驱动因素方面取得了巨大进展,但癌症仍然是全世界尚未攻克的难题之一。在这篇综述中,美国圣地亚哥州立大学生物学系的Adekunle Fiyin Ademikanra博士及其同事总结了癌症的起因(细胞、遗传和表观遗传学改变)、分类(癌症、肉瘤、淋巴瘤和白血病、母细胞瘤和生殖细胞肿瘤)、临床表现和治疗方法。作者重点介绍了最常用的化疗方案和其他治疗方案,以及肿瘤DNA中最容易发生基因改变的区域。
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00101-9

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册