Genome Instability & Disease Volume 5. Issue 5 简介
Dear colleagues,
We are pleased to announce the publication of GIAD Volume 5 Issue 5. Below, we provide brief summaries of the published articles.
1. Targeted DNA damage repair: old mechanisms and new opportunities in clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Jiahua Lv, Pengcheng Gong, Gongwei Jia & Wen Li
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has demonstrated resistance to conventional radiotherapy and chemotherapy in clinical settings. Professor Wen Li and her colleagues from Chongqing Medical University reviewed the epidemiology, clinical classification, diagnosis, and treatment strategies of ccRCC, with a focus on its molecular mechanisms and tumor microenvironment (TME). They particularly highlighted the role of DNA damage repair (DDR) in the progression of ccRCC, covering pathways such as mismatch repair, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, non-homologous end joining, and homologous recombination repair. Their work provides valuable insights for the clinical treatment of ccRCC.
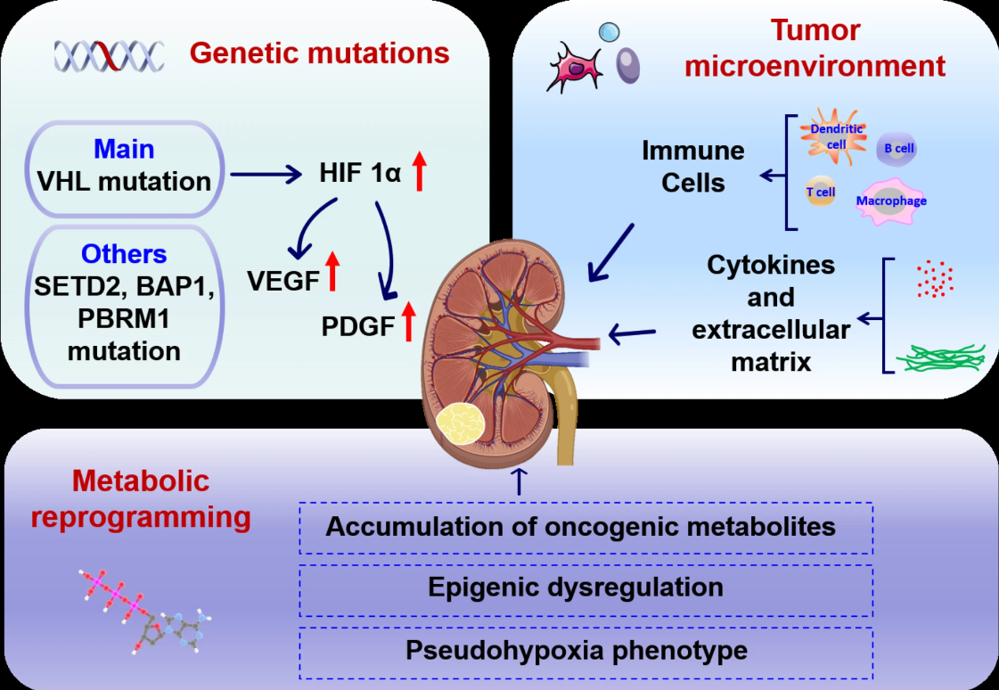
Fig.1 Risk factors for renal cancer.
透明细胞肾细胞癌(ccRCC)临床上对常规放化疗表现出耐药性,来自重庆医科大学的李雯教授团队总结了ccRCC流行病学、临床分类、诊断和治疗策略,重点介绍其分子机制和肿瘤微环境(TME),特别强调DDR在ccRCC发展中的作用,包括错配修复、碱基切除修复、核苷酸切除修复、非同源末端连接和同源重组修复,为ccRCC临床治疗提供参考。
 Prof. Wen Li
Prof. Wen Li
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00138-4
2. Mitochondrial dysregulation is a key regulator of gastric cancer subtype carcinogenesis| Karthik Balakrishnan
Mitochondrial function is closely linked to cancer development. Dr. Karthik Balakrishnan from the Saroj Institute of Technology and Management (SITM) in India investigated the role of mitochondrial dysregulation in the development of gastric cancer subtypes. He gathered a gene set associated with mitochondrial-dependent processes and conducted bioinformatics analyses across gastric cancer mRNA expression profiling cohorts from different continents. The study concludes that mitochondrial dysregulation plays dual roles in the carcinogenesis of diffuse and intestinal-type gastric tumors, offering new insights for targeted therapy development.
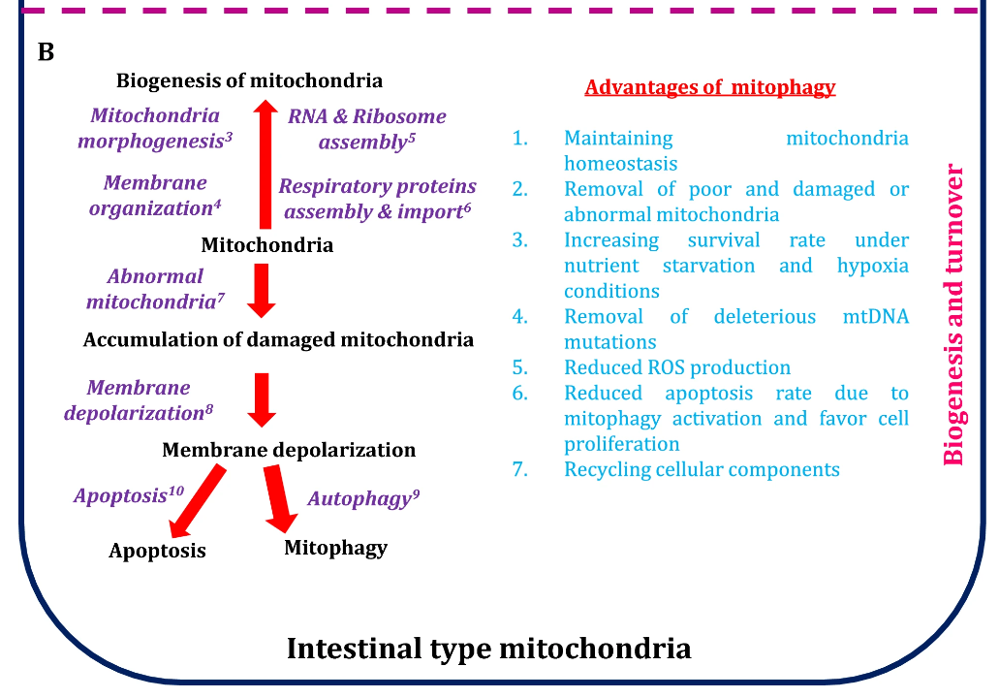 Fig.2 Mitochondrial biogenesis and turnover processes
Fig.2 Mitochondrial biogenesis and turnover processes
线粒体功能与癌症发生密切相关。来自Saroj 技术与管理学院(SITM)的Karthik Balakrishnan博士收集了与线粒体依赖过程相关的基因集,并在不同的癌症mRNA表达谱队列中进行了生物信息学研究,指出线粒体失调在弥漫性和肠型胃肿瘤的发生中起着双重作用,开发靶向治疗提供了新的见解。
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00136-6
3. Gene silencing by RNA interference: a review | Suresh Malakondaiah, Angeline Julius, Divyadharshini Ponnambalam, Summana Sree Gunthoti, Joshitha Ashok, Poorni Santhana Krishana & Jeyanthi Rebecca
RNA interference (RNAi) gene silencing has emerged as an effective method for regulating gene expression. Suresh Malakondaiah and his colleagues from the Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research (BIHER) in India have reviewed the role of RNAi in tackling genetic diseases, viral infections, cancer, and other conditions, as well as the challenges it faces in delivery, specificity, immunogenicity, and safety. This review provides valuable insights into RNAi, enhancing our understanding of its potential and informing future biological and medical research
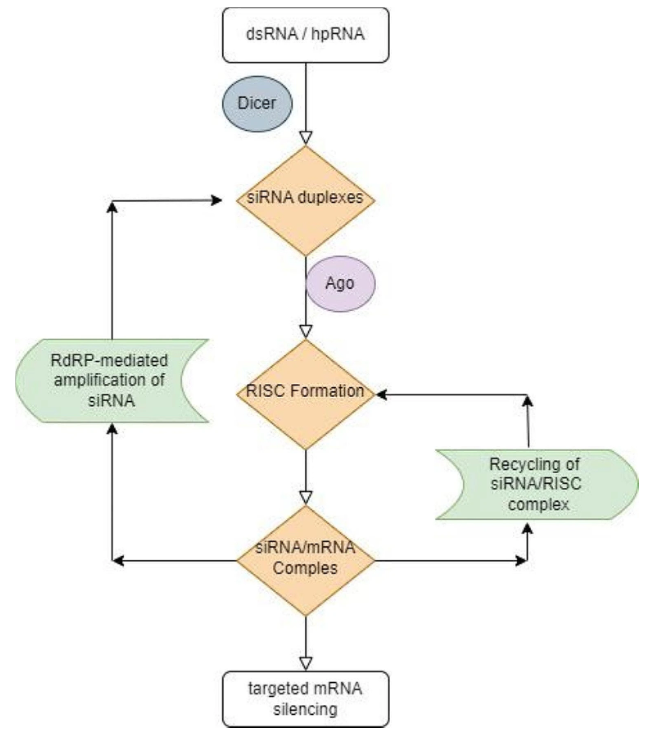
Fig. 3 Pathways of PTGS: RNA molecules are targeted for degradation, effectively reducing their abundance within the cell
RNA干扰(RNAi)的基因沉默已成为调节基因表达的有效方法。来自印度Bharath高等教育与研究学院(BIHER)的Suresh Malakondaiah和他的同事们总结了RNAi在解决遗传疾病、病毒感染、癌症和其他疾病方面发挥的作用,以及RNAi在递送、特异性、免疫原性和安全性方面存在的问题,帮助我们更加深入的了解RNAi和它在指导未来生物和医学研究中的作用。
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00135-7
4. Mitochondrial ND1 mutations and HSP60 and HSP70 mRNA expressions in patients with schizophrenia| Sevgi Karabulut Uzunçakmak, Ebubekir Dirican & Halil Özcan
Mitochondrial dysfunction is closely associated with schizophrenia. Sevgi Karabulut Uzun Çakmak from Bayburt University in Türkiye and colleagues found that, compared with a healthy control group, schizophrenia patients exhibit a high frequency of ND1 mutations, along with high expression of HSP60 and low expression of HSP70. These expression levels may serve as potential molecular markers for diagnosing schizophrenia. These findings offer important insights into the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in mental illness and inform potential treatment strategies for schizophrenia.
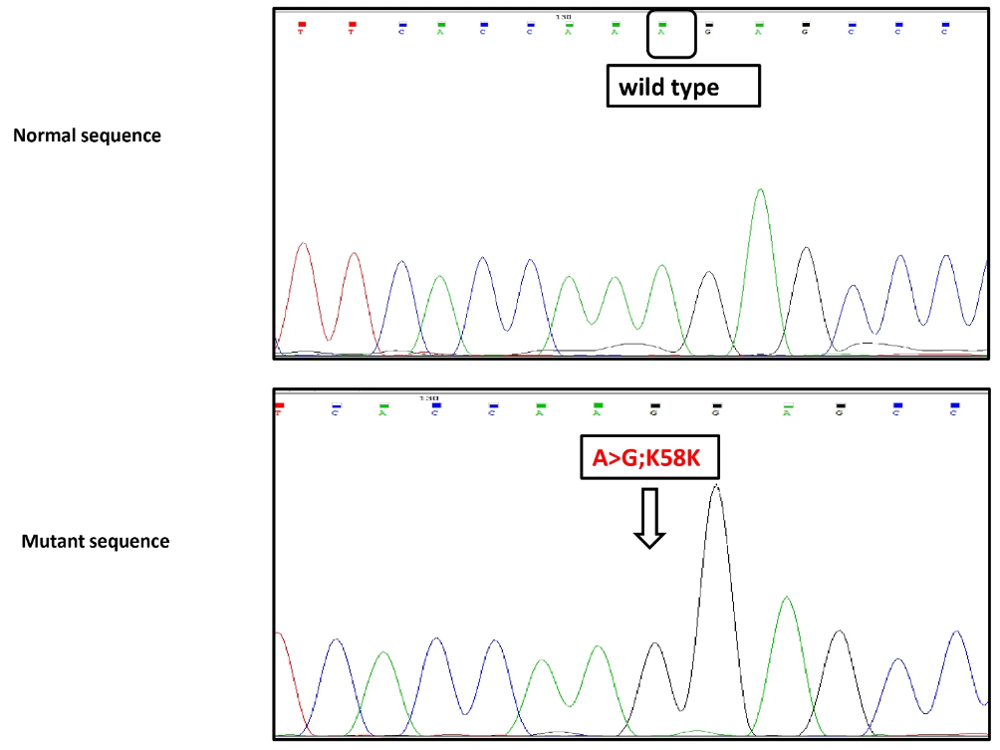 Fig. 4 Sequence analysis of A3480G, one of the most common mutations in patients with schizophrenia
Fig. 4 Sequence analysis of A3480G, one of the most common mutations in patients with schizophrenia
线粒体功障碍与精神分裂症密切相关,来自土耳其Bayburt大学的Sevgi Karabulut Uzunçakmak和同事通过Sanger测序,发现与健康对照组对比,精神分裂症患者存在高频率的ND1突变,且HSP60高表达而HSP70低表达,表明HSP60和HSP70的表达水平可能可以作为诊断精神分裂症的潜在分子标记物。这些发现为理解线粒体功能障碍在精神疾病中的作用和该疾病的治疗策略提供了重要参考。

Prof. Sevgi Karabulut Uzunçakmak
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00137-5
5. Harnessing DOT1L and RAP80: unveiling new insights into BRCA1-mediated DNA repair for cancer therapy | Peng Li & Xiaochun Yu
Professor Wei-Guo Zhu and his team recently published a study titled "DOT1L-mediated RAP80 methylation promotes BRCA1 recruitment to elicit DNA repair" in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). In this research, they identified a novel function of the histone methyltransferase DOT1L, which enhances the recruitment of the BRCA1-A complex to DNA damage sites by methylating RAP80. This discovery offers significant insights into the DNA Damage Response (DDR) mechanisms and holds potential implications for overcoming radiotherapy resistance in cancer treatment. Here, Professor Xiaochun Yu from Westlake University, provides his comment on the study, highlighting its substantial contribution to the understanding of DDR mechanisms.
 Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of the key role of DOT1L in the process of DDR
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of the key role of DOT1L in the process of DDR
近期朱卫国教授团队在PNAS上发表了一篇题为“DOT1L-mediated RAP80 methylation promotes BRCA1 recruitment to elicit DNA repair“的文章,对此,西湖大学的俞晓春教授予以点评,指出该文章在理解DNA损伤反应(DDR)的机制方面取得了重大进展,作者发现了组蛋白甲基转移酶DOT1L的新作用,通过RAP80的甲基化促进BRCA1-a复合物募集到DNA损伤位点,该发现对克服癌症治疗中的放疗耐药性具有深远的意义。

Prof. Xiaochun Yu
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-024-00139-3

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册