Genome Instability & Disease Volume 6. Issue 3 简介
1. Deciphering causal interactions between autoimmune and thyroid diseases: a Mendelian randomization analysis | Ren Jing, Yaoli Hou, Nan Wu, Qian Zhang, Shaojie Wu, Yang Wu & Shijian Yi
Autoimmune and thyroid disorders frequently co-occur, yet the directionality and underlying mechanisms of their association remain uncertain. In a comprehensive study at South China Hospital, Shenzhen University, Professor Shijian Yi and colleagues applied a bidirectional, two-sample Mendelian randomization framework. By integrating univariate, multivariate, and Bayesian weighting methods, they analyzed genetic and clinical data from over 10.3 million individuals. Their results robustly demonstrate a two-way causal relationship: autoimmune diseases increase the risk of thyroid dysfunction, and conversely, thyroid disorders elevate the likelihood of developing autoimmune conditions. These insights pave the way for more precise prevention strategies and support the implementation of integrated diagnostic and management protocols tailored to patients with these overlapping conditions.
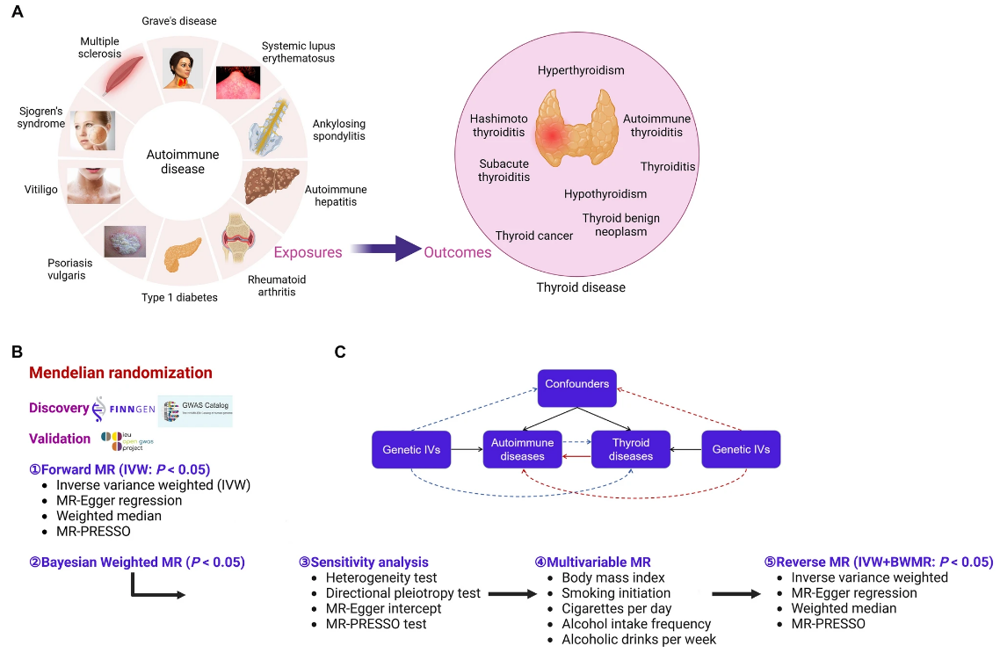 Study design overview: (A) exposures and outcomes for forward MR analysis; (B) analytical workflow; (C) bidirectional MR framework.
Study design overview: (A) exposures and outcomes for forward MR analysis; (B) analytical workflow; (C) bidirectional MR framework.
自身免疫疾病和甲状腺疾病经常同时出现,但它们的因果关系和机制还不清楚。来自深圳大学附属华南医院的易石坚教授团队利用双向双样本孟德尔随机化分析,整合了单变量、多变量和贝叶斯加权等方法,分析1030万人的数据,证实了自身免疫疾病和甲状腺疾病存在双向因果关系。这些发现为制定针对这两种共病患者的靶向预防策略和双重诊断临床方案提供了参考。

Prof. Shijian Yi
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00156-w
2. Identifying Melissa officinalis microRNAs as putative inhibitors in neurodegenerative disorders: a cross-kingdom approach | Aafrinbanu M. Shaikh, Darshana S. Musini, Rakesh M. Rawal & Saumya K. Patel
Melissa officinalis (lemon balm), a fragrant herb of the Lamiaceae family prized for its calming effects, is widely used across India. In a pioneering computational study at Gujarat University, Dr. Saumya K. Patel and colleagues mined the plant’s transcriptome to identify 29 conserved microRNAs. Through in silico target prediction, they found that these plant-derived miRNAs could potentially regulate 99 human genes implicated in key pathways of neurodegeneration, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, as well as in certain cancers. Notably, several miRNAs are predicted to modulate ESR1, CASP8, and SPTBN1, suggesting a cross-kingdom mechanism by which lemon balm may exert neuroprotective effects. These findings open new avenues for exploring plant miRNAs as therapeutic agents against neurodegenerative disorders.
Identifying Melissa officinalis microRNAs as putative inhibitors in neurodegenerative disorders: a cross-kingdom approach
柠檬香草Melissa officinalis是一种具有类似柠檬芳香的唇形科草本植物,具有镇静作用,在印度有广泛的应用。印度古吉拉特大学的Saumya K. Patel博士通过计算生物学方法,首次从柠檬香草(Melissa officinalis)转录组中识别出29个保守的microRNA,并预测其可靶向99个人类基因。研究发现这些miRNA可能通过调控ESR1、CASP8、SPTBN1等关键基因,影响神经退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病)和相关癌症的病理通路。该研究为植物源性miRNA的跨物种调控机制提供了新见解,并提示其潜在的治疗应用价值。
 Prof. Saumya K. Patel
Prof. Saumya K. Patel
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00157-9
3. Bioinformatics and next generation sequencing data analysis to identify key genes and pathways influencing in Parkinson's disease | Basavaraj Vastrad & Chanabasayya Vastrad
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder but its molecular causes remain incompletely understood. Drs. Basavaraj and Chanabasayya Vastrad at Chanabasava Nilaya, India, applied integrated bioinformatics and next-generation sequencing analyses to publicly available PD gene expression datasets. They identified 957 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), of which 478 were upregulated and 479 downregulated. Functional enrichment revealed that upregulated genes are primarily involved in nervous system development and cell–cell junction organization, while downregulated genes are associated with immune response and cellular stimulus response pathways. Further, protein–protein interaction and regulatory network analyses pinpointed 10 hub genes, including OTUB1 and PPP2R1A, which exhibited strong diagnostic potential in receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. These findings shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying PD and propose new candidate biomarkers for diagnosis and therapeutic targeting.
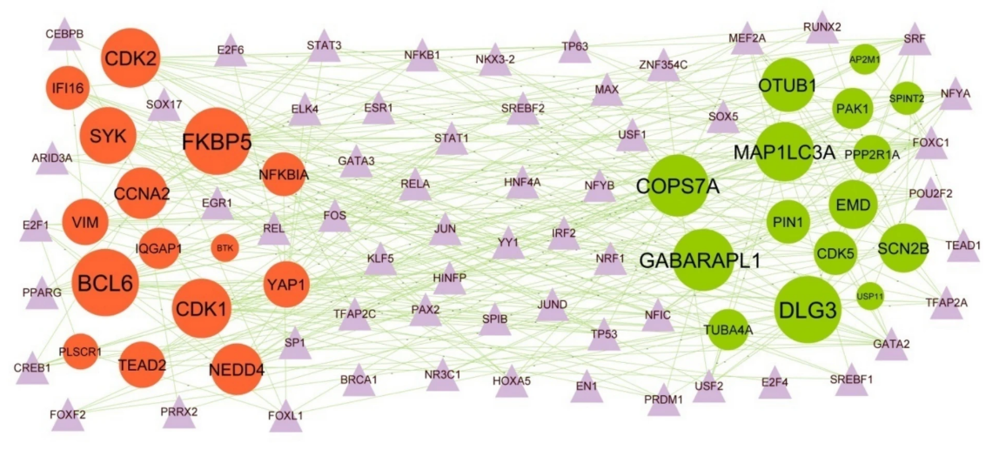
Target gene–TF regulatory network: purple triangle nodes represent key transcription factors; upregulated genes are green; downregulated genes are red.
帕金森病(PD)是最常见的神经退行性疾病,来自印度Chanabasava Nilaya的Basavaraj Vastrad 和Chanabasayya Vastrad博士通过生物信息学方法分析帕金森病(PD)的基因表达数据,识别出957个差异表达基因(DEGs),包括478个上调和479个下调基因。上调基因主要富集于神经系统发育、细胞连接等功能,下调基因则与免疫反应和刺激应答相关。研究进一步构建了蛋白质相互作用网络及调控网络,筛选出OTUB1、PPP2R1A等10个核心基因,并验证其具有良好的诊断价值。这些发现为帕金森病的分子机制研究和潜在生物标志物开发提供了新线索。
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00158-8
4. Hotspots and future trends of biomarker research in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis | Jingqi Liu, Yu Cai, Kaifang Wang, Beiyuan Chen, Nan Liu & Ou Sha
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the most prevalent malignancy of the oral and maxillofacial region. Professor Ou Sha and colleagues at Shenzhen University Medical School conducted a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of OSCC biomarker research from 1995 to 2024. Their systematic evaluation revealed that China leads in publication volume, whereas the United States dominates in international collaborations and total citation impact. Keyword co-occurrence analysis identified five principal research clusters, with emerging hotspots in the tumor microenvironment, liquid biopsy techniques, salivary biomarkers, and immunotherapy. Among established markers, p53, p16, and Cyclin D1 remain the most extensively studied, while attention to novel candidates such as miR-21 and miR-31 is rapidly increasing. These insights offer valuable guidance for prioritizing future biomarker discovery and translating findings into more precise diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for OSCC.
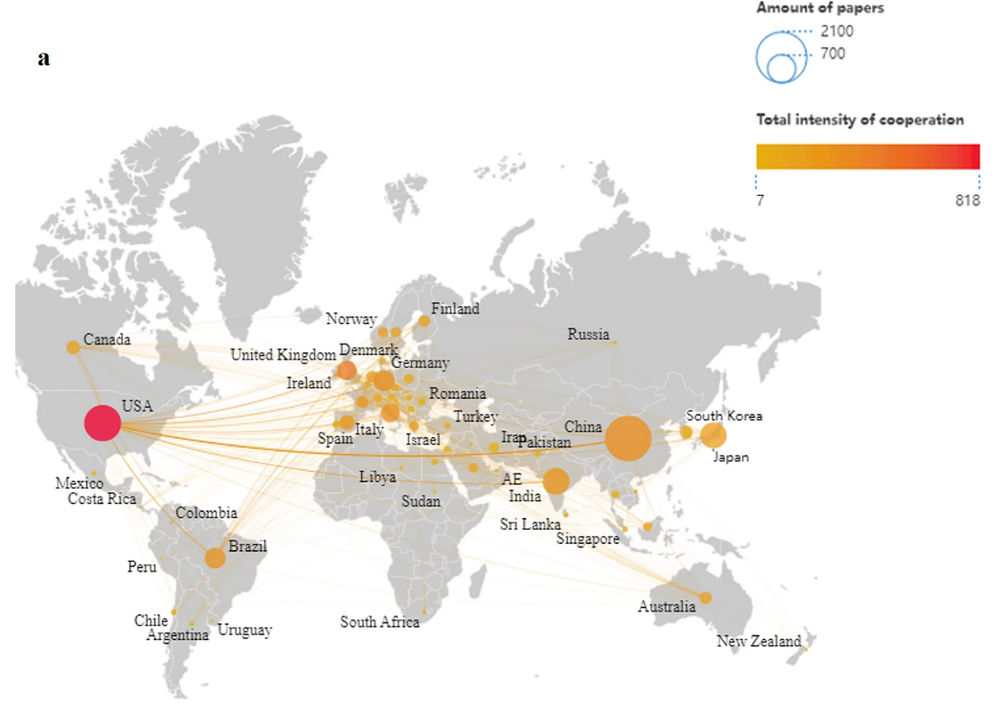 Global map illustrating the number of articles published per country (circle size) and the overall intensity of international collaborations (color scale); generated using Scimago Graphica.
Global map illustrating the number of articles published per country (circle size) and the overall intensity of international collaborations (color scale); generated using Scimago Graphica.
口腔鳞状细胞癌是口腔颌面部最常见的恶性肿瘤,来自深圳大学医学部口腔学院的沙鸥教授团队通过文献计量学方法系统分析了1995至2024年间口腔鳞状细胞癌(OSCC)生物标志物领域的研究趋势与热点,研究显示,中国在发文量上领先,而美国在国际合作和总引用次数方面表现突出。关键词分析揭示了五个主要研究主题集群,近期热点集中在“肿瘤微环境”、“液体活检”、“唾液生物标志物”和“免疫治疗”等方面。P53、P16、Cyclin D1等分子是研究最广泛的生物标志物,而miR-21、miR-31等新兴分子也受到越来越多关注。该研究为未来OSCC的精准诊断和治疗方向提供了重要参考。
 Prof. Ou Sha
Prof. Ou Sha
全文链接: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00159-7
5. Aberrant DNA methylation in adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and the therapeutic potential of hypomethylating agents| Haiyu Song & Li Yu
Abnormal DNA methylation is a hallmark of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Professor Li Yu and colleagues at Shenzhen University General Hospital conducted a systematic review of the prevalence, prognostic significance, and therapeutic implications of DNA methylation aberrations in adult B-cell ALL (B-ALL). They found that DNA hypermethylation correlates with older age at diagnosis, poorer overall survival, and an elevated risk of relapse, particularly among high-risk cytogenetic subgroups. Key genes frequently hypermethylated include TP73, P15 (CDKN2B), DLC1, and RASSF6, underscoring their promise as prognostic biomarkers. Moreover, the authors highlight emerging evidence for hypomethylating agents, such as decitabine and azacitidine, in relapsed or refractory adult B-ALL. When combined with conventional chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, or CAR-T cell therapy, these agents have demonstrated encouraging response rates and tolerability, offering a novel avenue to overcome methylation-driven resistance.
异常的DNA甲基化在急性淋巴细胞白血病(ALL)中普遍存在,来自深圳大学总医院的于力教授团队系统综述了成人B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(B-ALL)中异常DNA甲基化的作用及其临床意义。研究表明,DNA高甲基化与患者年龄增长、不良预后和复发风险密切相关,尤其在高危亚型中尤为显著。作者重点讨论了多个关键基因(如TP73、P15、DLC1、RASSF6等)的甲基化状态及其作为预后生物标志物的潜力。此外,他们强调低甲基化药物(如地西他滨和阿扎胞苷)在治疗复发/难治性成人B-ALL中的临床应用前景,包括与化疗、移植或CAR-T疗法联合使用的积极效果。
 Prof. Li Yu
Prof. Li Yu
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00152-0
6. Histone lysine succinylation: a comprehensive review of enzymatic pathways and disease associations | Minghui Zhang, Huacai Peng, Zhouzhu Liang & Jinke Gu
Lysine succinylation (Ksuc) is a recently characterized histone post-translational modification that profoundly influences chromatin dynamics. In this review, Professor Jinke Gu and colleagues at Shenzhen University Medical School trace the discovery of Ksuc and catalog its principal histone targets, most notably H3K79 and H3K122. They detail the “writers” of this mark, including the lysine acetyltransferases KAT2A, HAT1, and p300, which transfer succinyl groups from succinyl-CoA to specific lysine residues. Conversely, the “erasers” of succinylation comprise the sirtuins SIRT5 and SIRT7, as well as class I histone deacetylases HDAC1, HDAC2, and HDAC3. By introducing a bulky, negatively charged succinyl moiety, Ksuc loosens nucleosomal packing, thereby enhancing gene transcription and facilitating DNA damage repair. Importantly, aberrant succinylation has been implicated in diverse pathologies. Elevated Ksuc levels correlate with tumor progression in various cancers, while dysregulated succinylation also appears in chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. These disease associations, together with the reversible nature of the modification, highlight histone succinylation as a promising epigenetic target for novel therapeutics.
.
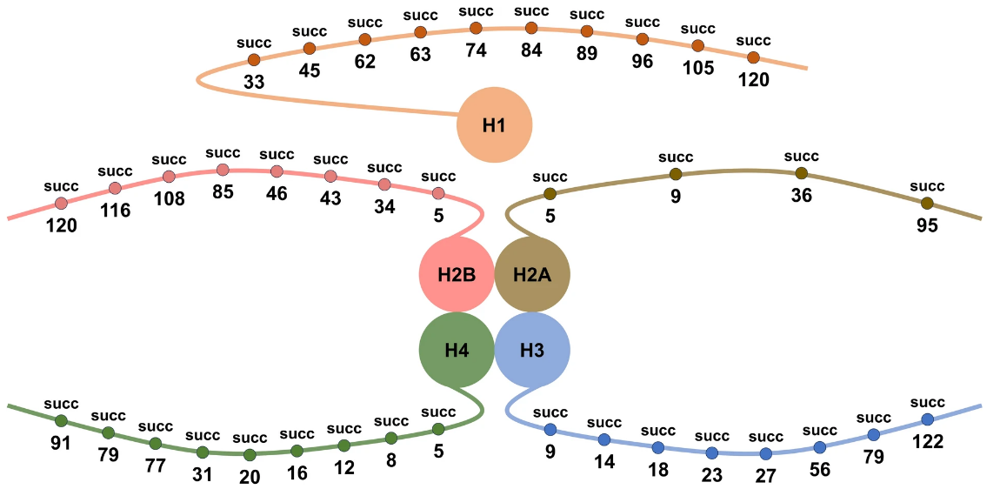 Known histone succinylation sites reported in the literature.
Known histone succinylation sites reported in the literature.
赖氨酸琥珀酰化(Ksuc)是最近发现的一种组蛋白翻译后修饰(HPTMs),深圳大学医学部的谷金科团队系统总结了Ksuc 的研究进展,包括其作为一种新兴组蛋白修饰的发现历程、主要修饰位点(如H3K79和H3K122)及其调控机制。作者指出琥珀酰化由琥珀酰-CoA作为供体,通过KAT2A、HAT1和p300等酶催化,并可被SIRT5、SIRT7和HDAC1/2/3等去琥珀酰酶逆转。该修饰通过改变染色质结构和可及性,促进基因转录和DNA损伤修复,并与癌症、HBV感染等疾病密切相关,具有成为治疗靶点的潜力。

Prof. Jinke Gu
全文链接: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-025-00148-w

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册