Genome Instability & Disease Volume 2. Issue 6 简介
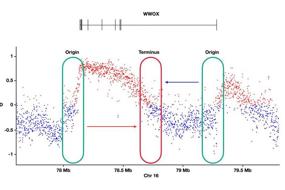
1. Chromosome instability induced by mutations in TAD anchors leads to tumors | Andrey N. Luchnik
A TAD anchor is a type of DNA loop or gene block that is found attached to the chromatid axis. When this anchor falls off, mutations can be induced in the TAD anchor gene, leading to genetic chromosomal instability. In this review, Dr. Andrey N. Luchnik from the Korzov Institute of Developmental Biology of the Russian Academy of Sciences introduce us to the relationship between TAD anchor gene mutations, chromosomal instability and tumor growth stimulation. The article helps us to better understand the relationship between hereditary chromosomal instability and tumorigenesis.
TAD锚是一类附着在染色单体轴上的DNA环或基因块,当其脱落时往往会引起TAD锚基因突变,从而导致遗传性染色体不稳定。在这篇综述里,来自俄罗斯科学院科尔佐夫发育生物学研究所的Andrey N. Luchnik博士介绍了TAD锚基因突变与染色体不稳定性以及肿瘤生长刺激之间的关系,帮助我们更好地理解遗传性染色体不稳定性与肿瘤发生之间的关系。

Dr. Andrey N. Luchnik
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00050-1
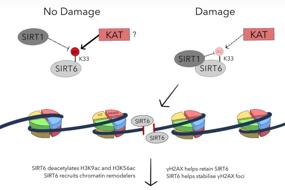
2. Genome instability in pathogenesis of tuberculosis | Kehong Zhang, Yuping Ning, Fanhui Kong, Xinchun Chen & Yi Cai
Understanding tuberculosis pathogenesis and the emergence of drug-resistant strains is a global priority. In this review, Dr. Yi Cai and colleagues from Shenzhen University highlight the role of genome instability in tuberculosis pathogenesis. They focus on how Mtb hypermutability is often associated with the emergence of resistant bacteria. They also discuss how an Mtb infection can induce genome instability of host cells and the formation of giant cells. Finally, they shed light on the development of new strategies for TB treatment.
结核分枝杆菌 (Mtb)的基因组稳定性维持与结核病发病机制密切相关,在这篇综述里,深圳大学的蔡毅博士向我们介绍了基因组不稳定性在结核病发病机制中的作用,有助于我们了解结核病发病机制及最新的治疗策略。

Dr. Yi Cai
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00057-8
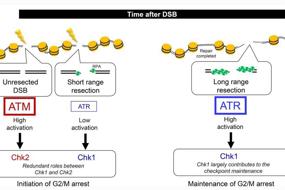
3. Nature of spontaneously arising single base substitutions in normal cells | Shunichi Takeda & Yang Luan
The number of gene mutations in normal somatic cells increases linearly with age, and most of them appear in the form of single base substitutions. In this review, Dr. Yang Luan from Shanghai Jiaotong University and Professor Shunichi Takeda from Shenzhen University outline the nature of spontaneous SBSs in normal tissues. They also explain the causes, mechanisms and repair pathways involved that aim to suppress mutagenesis. Finally, they speculate on some of the current unresolved questions in this area that warrant further research.
正常体细胞发生基因突变的数量随着年龄的增加而线性上升,且多数是以单碱基替换(SBS)的形式出现。在这篇综述里,上海交通大学的栾洋研究员和深圳大学的Shunichi Takeda教授向我们介绍了各种正常组织自发产生SBS,以及发生的原因、机制和修复途径,帮助我们更好地理解基因突变的机制和治疗策略。

Prof. Shunichi Takeda

Dr. Yang Luan
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00056-9
4.Terpenoids-enriched fraction of Celastrus orbiculatus sensitizes gemcitabine by disrupting Chk1/RAD51-mediated DNA damage response in pancreatic cancer |Yang Zhao, Zhuangzhuang Jiang, Tengyang Ni, Wei Jiang, Kehui Zhou, Yuping Liu, Yanqing Liu & Li Tao
Total Terpenoids of C. orbiculatus (TTC) is a total terpenoid compound extracted from the Celastrus orbiculatus stem. Now, Li Tao, Yanqing Liu and colleagues from Yangzhou University have reported that the combination of TTC and the anticancer drug gemcitabine has a sensitizing effect on pancreatic cancer. They revealed the underlying mechanism of sensitization to be based on the ability of TTC to inhibit Chk1/RAD51 and thus promote the accumulation of γH2AX. These data highlight how TTC and molecules involved in DNA damage and repair could be targeted to confer chemosensitivity to gemcitabine in patients with pancreatic cancer.
TTC (Total Terpenoids of C.orbiculatus)是从Celastrus orbiculatus的茎部提取的总萜类化合物。来自扬州大学的陶丽和刘延庆课题组报道了TTC与抗癌药物吉西他滨联用具有增敏效果,并阐明其作用机理:TTC能够抑制 Chk1/RAD51,促进γH2AX 的积累,并逆转由吉西他滨引发的与复制应激相关的 DNA 损伤反应。该发现为吉西他滨在胰腺癌的临床治疗提供了新的参考。

Prof. Li Tao

Prof. Yanqing Liu
全文下载:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-021-00055-w

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册