Genome Instability & Disease Volume 3. Issue 4 简介
1. p53 regulation by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications | Ying Wang, Chenlu Zhang, Jiabao Wang & Jiang Liu
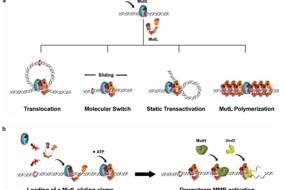
Tumor protein p53 is a critical tumor suppressor gene, and thus is known as the “guardian of the genome”. In this review, Professor Jiang Liu and colleagues at Hangzhou Normal University, China, introduce the various post-translational modifications (PTMs) that can occur to p53. The researchers pay particular attention to p53 ubiquitination and UBL modification, which have major roles in regulating p53 function. This review provides an excellent overview of the relationship between p53 regulation and tumorigenesis.
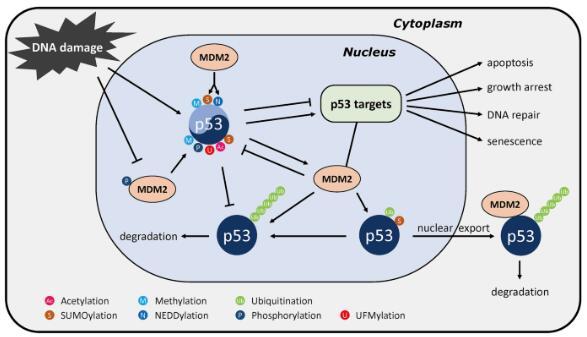
Fig. 1 The p53 network.
p53是调控肿瘤发生的关键基因,在这篇综述里,来自杭州师范大学的刘江教授向我们介绍了p53的各种翻译后修饰(PTMs), 尤其是泛素化和UBL修饰对p53发挥调控功能的影响,帮助我们更好的理解p53调控和肿瘤发生之间的关系。

刘江教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00067-0
2.Epithelial tumor compartment- and adjacent stromal compartment-specific expression of PARP1 in different anatomical sites in patients with HGSOC| Caglar Berkel & Ercan Cacan
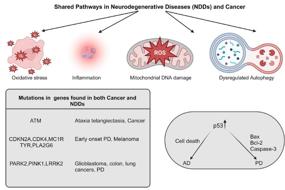
PARP1 is typically overexpressed in ovarian cancer (OC). As such, PARP inhibitors, including olaparib, rucaparib, and niraparib, are currently used as first-line OC treatments. However, the expression pattern of PARP1 in terms of epithelial tumor versus stromal, anatomical site and histotype-specific expression is unknown. Caglar Berkel and Ercan Cacan at Tokat Gaziosmanpasa University, Turkey, have now addressed this knowledge gap. They compared PARP1 protein levels in OC epithelial tumors and adjacent non-malignant stroma at four different anatomical locations in high-grade serous OC and normal tissues. The researchers found that PARP1 protein expression was, in fact, increased in epithelial tumors at all sites compared to normal tissues. The most significant elevation in PARP1 expression was seen in the omentum. This finding sheds light on the roles and mechanisms of PARP in OC pathogenesis.
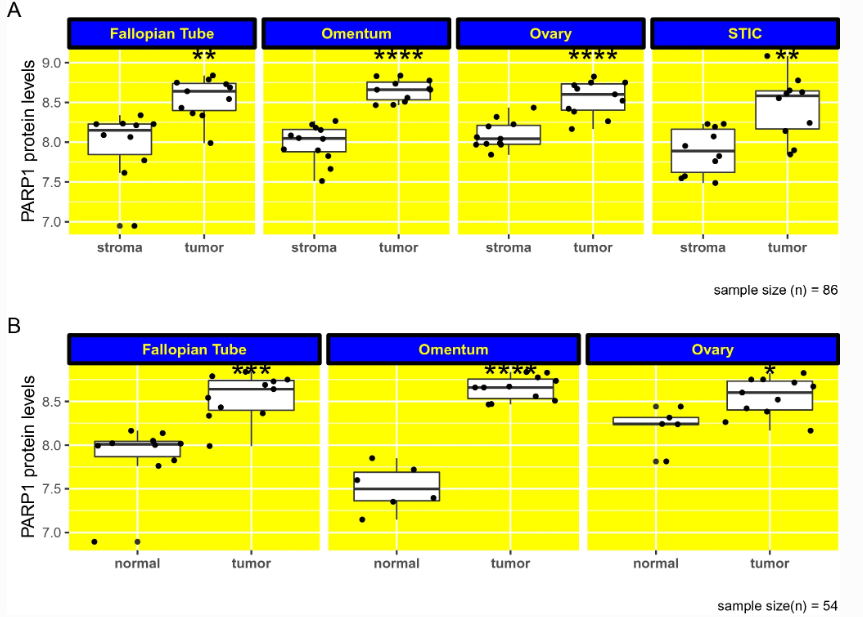
Fig. 2 PARP1 protein levels are higher in tumors compared to adjacent non-malignant stroma in HGSOC
PARP抑制剂(olaparib, rucaparib and niraparib)是目前治疗卵巢癌(OC)的一线药物,既有的研究表明,PARP1在OC中表达增加,但未研究其隔室(上皮肿瘤与间质)、解剖部位(输卵管、网膜、卵巢和浆液性输卵管原位癌)和组织型特异性表达。来自土耳其Tokat Gaziosmanpasa大学的Caglar Berkel 和 Ercan Cacan研究了PARP1在卵巢癌上皮肿瘤、 HGSOC中四个不同解剖位置的相邻非恶性基质以及正常组织中的蛋白水平,发现PARP1蛋白在上述部位中呈递减分布,该发现验证了PARP抑制剂治疗卵巢癌的作用机理,对卵巢癌治疗及用药提供了参考。

Ercan Cacan教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00075-0
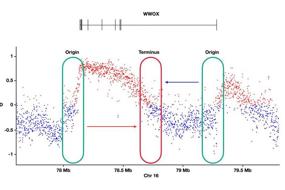
3.Aberrant DNA methylation in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia | Shujiao He, Jingfeng Zhou & Li Yu
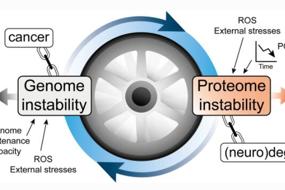
Abnormal DNA methylation is an important feature of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). According to DNA methylation sequencing, t(8;21)AML has a unique DNA methylation signature, but its causes and mechanisms are poorly understood. In this review, Prof. Li Yu and colleagues at Shenzhen University General Hospital, China, summarize the latest progress in our understanding of how DNA methylation is regulated in t(8;21)AML and discuss its potential clinical significance.
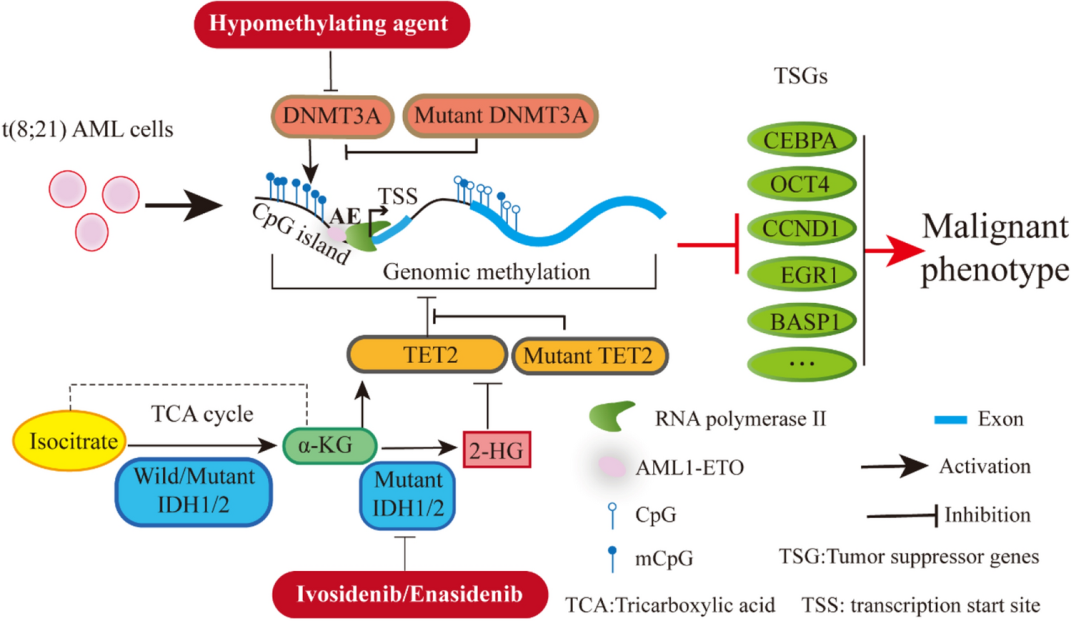
Fig. 3 DNA methylation modulation in t(8;21) AML
DNA甲基化异常是急性髓系白血病(AML)的一个重要特征。根据DNA甲基化测序,t(8;21)AML具有独特的DNA甲基化特征,但其原因和机制至今仍缺乏了解。在这篇综述里,来自深圳大学总医院的于力教授向我们总结了目前关于t(8;21)AML中DNA甲基化调节的知识,并讨论了其潜在的临床意义。

于力教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00072-3
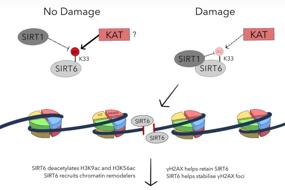
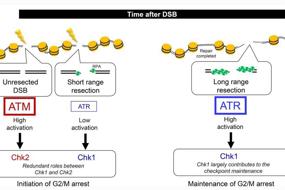
4. Dynamic recruitment of UFM1-specific peptidase 2 to the DNA double-strand breaks regulated by WIP1 | Bo Qin, Jia Yu, Fei Zhao, Jinzhou Huang, Qin Zhou & Zhenkun Lou
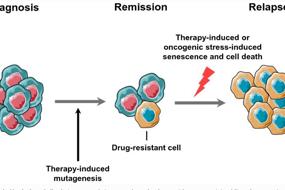
Ufmylation acylation ligase UFM1-specific peptidase 2 (UfSP2) inhibits ATM activation to regulate the DNA damage response, but the underlying mechanism is unclear. Here, Zhenkun Lou and colleagues at the Mayo Clinic, USA, show that in the absence of double strand breaks (DSBs), UfSP2 binds to the MRN complex. Upon irradiation-induced DSB formation, UfSP2 is phosphorylated by ATM, and subsequently dissociates from the MRN complex. WIP1 can remove this phosphorylation event from UfSP2, allowing for H4 deufmylation and suppressed ATM activation. These findings expose the subtle negative modulation mechanism of UfSP2 on ATM activation, reconstructs the ATM activation pathway, and makes important revisions to the DNA damage repair mechanisms.
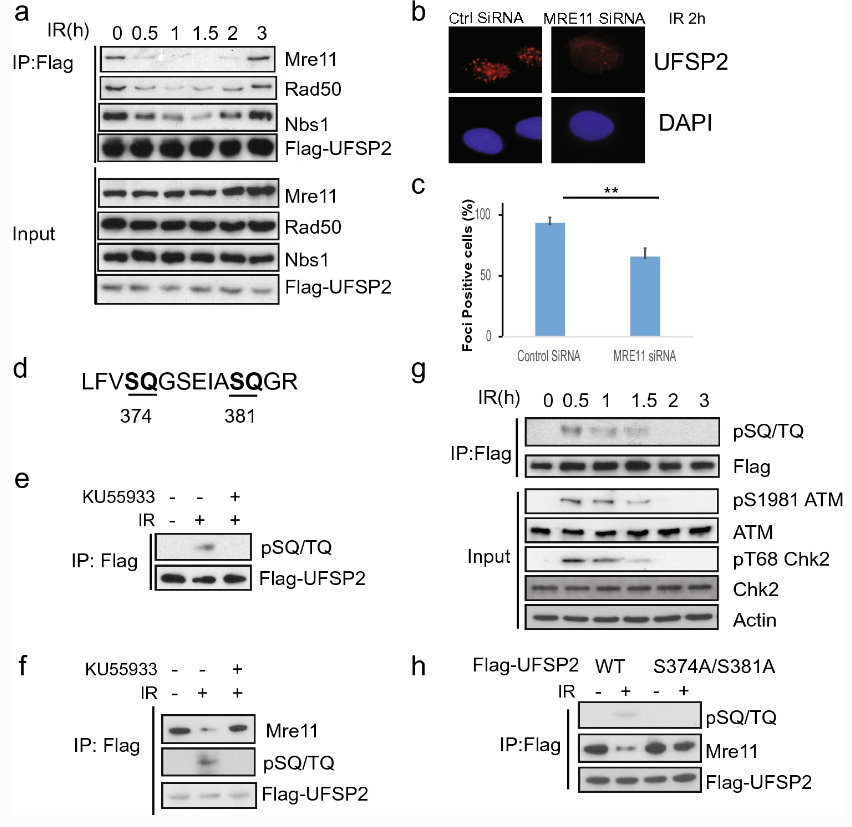
Fig. 4 The interaction of UfSP2 with the MRN complex is regulated by ATM-mediated phosphorylation
DNA双链断裂后的修复是一个复杂的过程,已知UFM酰化连接酶UFM1特异性肽酶2(UfSP2)能够抑制ATM激活,但UfSP2如何准确调节DNA损伤反应的机制仍未清楚。来自美国Mayo Clinic肿瘤科的楼振坤团队发现在没有DSB的情况下,UfSP2与MRN复合物结合,DSB出现诱导UfSP2磷酸化,导致UfSP2从MRN复合物解离,去磷酸化H4并抑制ATM激活,进而影响DNA损伤修复进程。该报道解析了UfSP2对ATM激活的微妙负调制机制,并重新构建了ATM激活途径,对DNA损伤修复机制做了重要修正。

楼振坤教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-022-00076-z

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册