Genome Instability & Disease Volume 4. Issue 5 简介
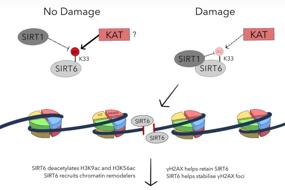
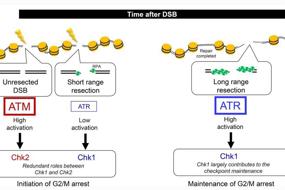
1. Novel insights into DNA damage repair defects in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: from the molecular basis to therapeutic opportunities | Qi Liu, Nan Zuo, Xinghan Li, Yongqiang Deng, Lanlan Wei & Lin Ma
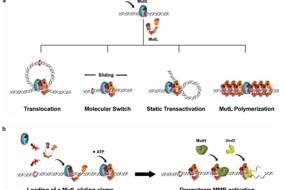
The occurrence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is closely related to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Indeed, it seems that patients with HNSCC and concurrent HPV infection have a significantly better prognosis after receiving genotoxicity therapy than HPV-negative patients. In this review, Professor Lin Ma (Shenzhen University General Hospital) and colleagues explain why this paradigm might be the case, discussing the impact of HPV infection on the DNA damage repair (DDR) system. Then, they discuss the related treatment strategies for HNSCC, providing valuable guidance and reference for the clinical treatment of this disease.
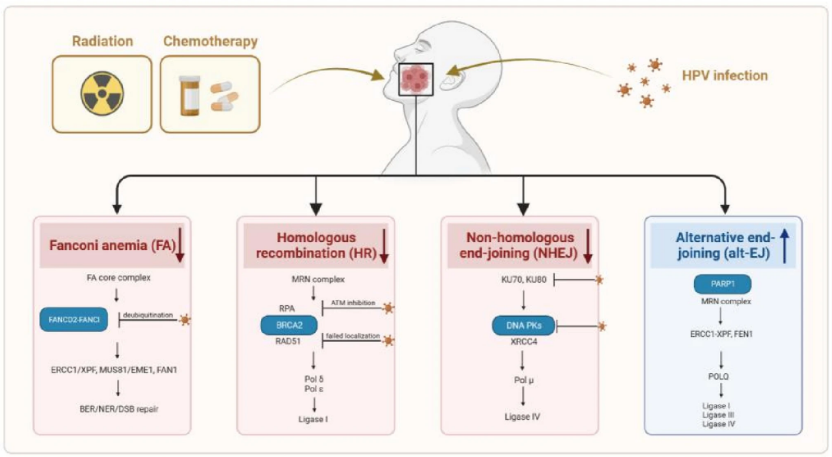
Fig.1 Schematic depicting how HPV infection affects DNA damage repair in the context of HNSCC.
头颈部鳞状细胞癌(HNSCC)的发生与人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)密切相关。有研究报道HPV阳性的HNSCC患者与阴性患者相比,接受基因毒性治疗后的预后明显更好。来自深圳大学总医院的马琳教授和深圳第三人民医院的魏兰兰教授团队向我们介绍了HPV对HNSCC的DNA损伤修复(DDR)和相关治疗策略的影响,为HNSCC的治疗提供指导与参考。

马琳副研究员

魏兰兰教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00109-1
2. The mechanism and consequences of BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma| Ksenia Golub, Weiyu Bai, Zhimeng Zhang, Huilin Xiao, Rongyuan Sun, Junling Shen & Jianwei Sun
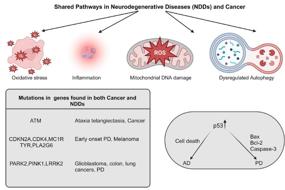
Vemurafenib is a BRAFV600E selective kinase inhibitor (BRAFi) that is commonly used to treat BRAFV600E melanoma patients. Unfortunately, around 50% of affected patients develop vemurafenib treatment-induced resistance and go on to exhibit disease progression within 6 months. In this review, Professor Jianwei Sun and colleagues from Yunnan University, summarize the underlying mechanisms of vemurafenib treatment-induced resistance that impact on the MAPK, EGF/EGFR, IL6/STAT3 pathways. They then discuss the consequences of vemurafenib treatment-induced resistance in melanoma, and offer their guidance on how we might intervene on this paradigm going forward.
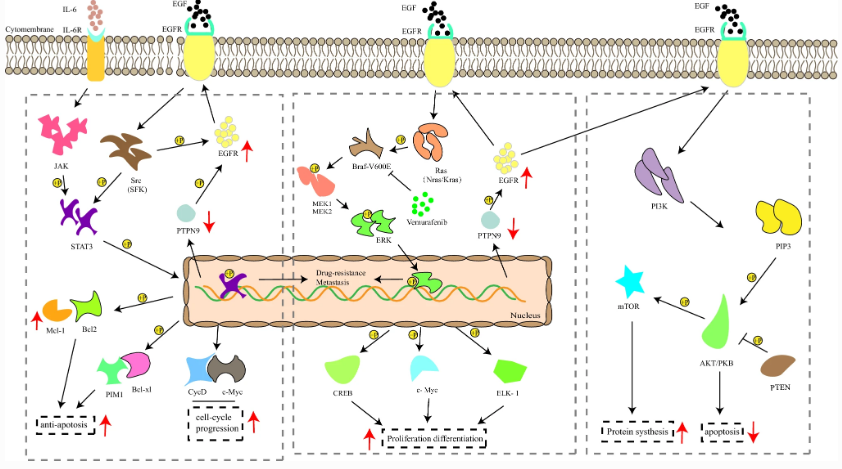
Fig.2 Vemurafenib resistance reactivates multiple pathways to overcome therapeutic efficiency.
Vemurafenib是一种针对BRAF V600E靶点的黑色素瘤药物,50%的患者在接受该药物治疗6个月左右时出现耐药情况。来自云南大学的孙建伟教授团队总结了Vemurafenib在黑色素瘤中耐药性的机制和后果,为BRAF抑制剂耐药性的干预提供指导。

孙建伟教授
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00105-5
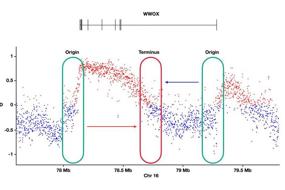
3. Chromatin-based DNA replication initiation regulation in eukaryotes | Lei Hao, Ruixin Fang & Haizhen Long
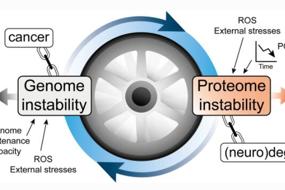
DNA replication is a complex process that must be regulated by multiple factors to ensure genome integrity. During the G1 phase of the cell cycle, the Origin Recognition Complex (ORC) must recognize and subsequently mark specific regions on the chromosome. Later in S phase, these marked replication origins are activated. In this review, Haizhen Long and colleagues (Shenzhen Bay Laboratory) detail precisely how this mechanism of replication origin selection and activation is achieved. They focus particularly on the important layer of epigenetic regulation that helps to direct DNA replication initiation in eukaryotes, giving insight into the necessary histone modifications that occur during this process.
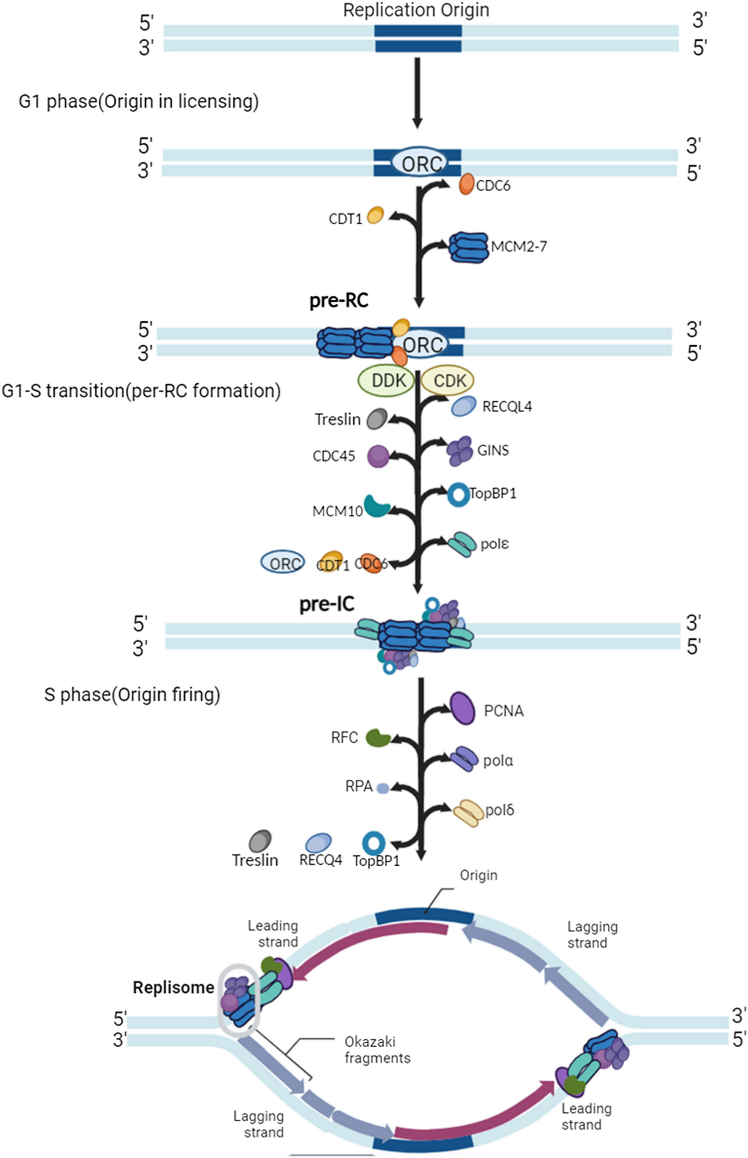
Fig. 3 DNA replication initiation in mammals.
DNA复制是一个复杂的过程,受到多种因素的调控。来自中国深圳湾实验室的龙海珍研究员向我们介绍了DNA复制起源的选择和激活过程,以及真核生物中DNA复制启动的表观遗传学调控机制,重点关注了组蛋白及组蛋白修饰在DNA复制过程中的调控作用。

龙海珍研究员
全文链接: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00108-2
4. In Silico design and characterization of RAD51 protein inhibitors targeting homologous recombination repair for cancer therapy | Harsimrat Kaur, Harsimran Kaur, Preeti Rajesh & Changanamkandath Rajesh
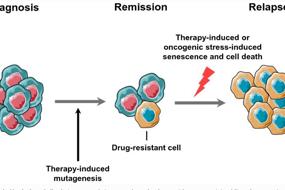
DNA damage repair (DDR) is normally a beneficial response for organisms to ensure genome integrity. However, the activation of DDR pathways can also be a driving force behind treatment resistance, in particular to cancer radiotherapy and chemotherapy. In this original research article, Dr. Preeti Rajesh (Chandigarh University, India) Dr. Changanamkandath Rajesh (MIT School of Bioengineering Sciences and Research, India) describe how they designed binding ligand peptides as DDR blockers targeting RAD51. Their data help explain how targeting the homologous recombination DDR pathway by functional inhibition of RAD51 proteins (either directly via its ATPase activity or via its interaction BRCA2) can effectively prevent the repair of radiotherapy- or chemotherapy-induced damage and ensure cancer cell death.
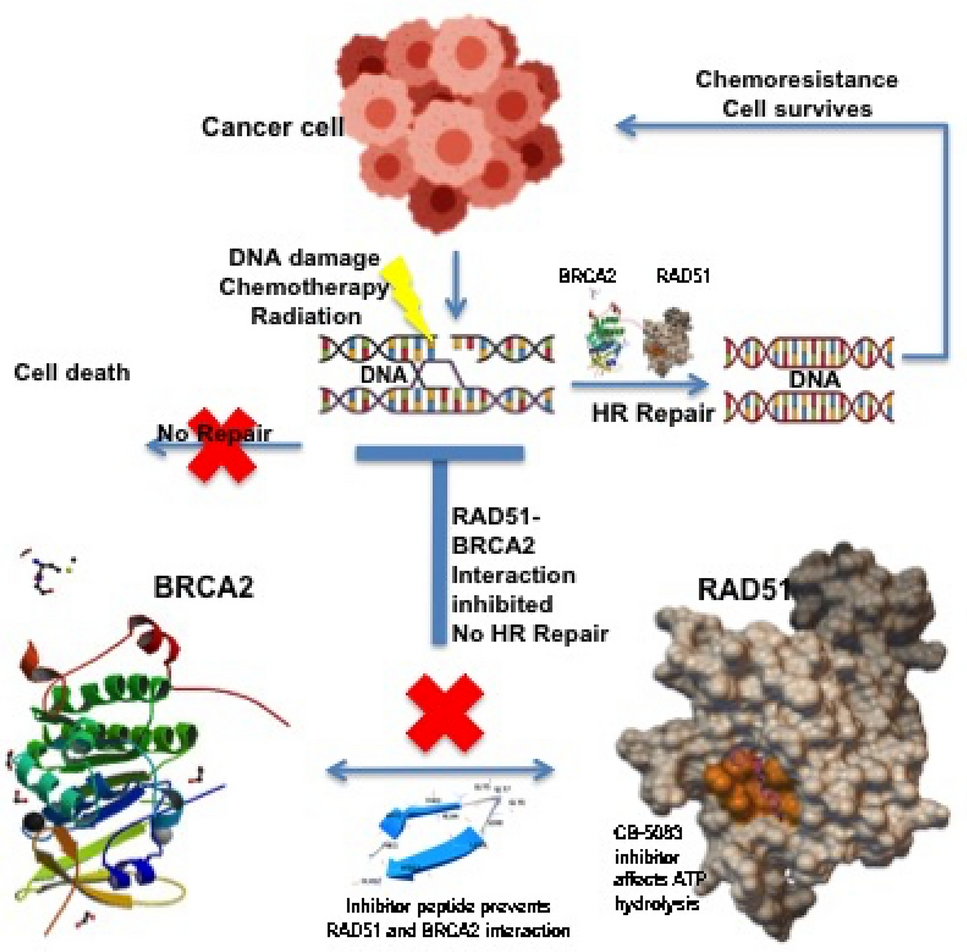
Fig. 4 Schematic Representation of the proposed mechanism that will enhance the chemotherapeutic regimen by preventing chemo-resistance.
DNA损伤修复(DDR)正常情况下对于生物是有益的,但在肿瘤治疗中,却是放化疗产生耐药性的重要原因。来自印度Chandigarh大学的Preeti Rajesh博士和印度设计与技术大学生物工程科学与研究学院的Changanamkandath Rajesh博士针对RAD51靶点设计了结合配体多肽作为DDR阻断剂,并讨论了其他化学抑制剂的阻断作用,为潜在的组合化疗提供参考。
全文链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42764-023-00106-4

用户登录
还没有账号?
立即注册